Ideal for Kidney Tissue Homogenization
Do you spend lots of time and effort homogenizing kidney tissue samples? The Bullet Blender® tissue homogenizer delivers high quality and superior yields. No other homogenizer comes close to delivering the Bullet Blender’s winning combination of top-quality performance and budget-friendly affordability. See below for a kidney tissue homogenization protocol.
Save Time, Effort and Get Superior Results with
The Bullet Blender Homogenizer
Consistent and High Yield Results
Run up to 24 samples at the same time under microprocessor-controlled conditions, ensuring experimental reproducibility and high yield. Process samples from 10mg or less up to 3.5g.No Cross Contamination
No part of the Bullet Blender ever touches the tissue – the sample tubes are kept closed during homogenization. There are no probes to clean between samples.Samples Stay Cool
The Bullet Blenders’ innovative and elegant design provides convective cooling of the samples, so they do not heat up more than several degrees. In fact, our Gold+ models hold the sample temperature to about 4ºC.Easy and Convenient to Use
Just place beads and buffer along with your tissue sample in standard tubes, load tubes directly in the Bullet Blender, select time and speed, and press start.Risk Free Purchase
Thousands of peer-reviewed journal articles attest to the consistency and quality of the Bullet Blender homogenizer. We offer a 2 year warranty, extendable to 4 years, because our Bullet Blenders are reliable and last for many years.Kidney Tissue Homogenization Protocol
Sample size |
See the Protocol |
| microcentrifuge tube model (up to 300 mg) | Small kidney samples |
| 5mL tube model (100mg - 1g) | Medium kidney samples |
| 50mL tube model (100mg - 3.5g) | Large kidney samples |
What Else Can You Homogenize? Tough or Soft, No Problem!
The Bullet Blender can process a wide range of samples including organ tissue, cell culture, plant tissue, and small organisms. You can homogenize samples as tough as mouse femur or for gentle applications such as tissue dissociation or organelle isolation.

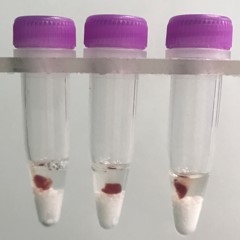

Kidney tissue pieces (on beads in upper photo) are completely homogenized into the buffer (slightly darker in lower photo).
Want more guidance? Need a quote? Contact us:

Bullet Blender Models
Select Publications using the Bullet Blender to Homogenize Kidney Tissue
2474232
kidney
1
apa
50
date
desc
3176
https://www.nextadvance.com/wp-content/plugins/zotpress/
%7B%22status%22%3A%22success%22%2C%22updateneeded%22%3Afalse%2C%22instance%22%3Afalse%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22request_last%22%3A0%2C%22request_next%22%3A0%2C%22used_cache%22%3Atrue%7D%2C%22data%22%3A%5B%7B%22key%22%3A%222JKV27ZR%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Coughlan%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222016-05-01%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A3%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3ECoughlan%2C%20M.%20T.%2C%20Nguyen%2C%20T.-V.%2C%20Penfold%2C%20S.%20A.%2C%20Higgins%2C%20G.%20C.%2C%20Thallas-Bonke%2C%20V.%2C%20Tan%2C%20S.%20M.%2C%20Bergen%2C%20N.%20J.%20V.%2C%20Sourris%2C%20K.%20C.%2C%20Harcourt%2C%20B.%20E.%2C%20Thorburn%2C%20D.%20R.%2C%20Trounce%2C%20I.%20A.%2C%20Cooper%2C%20M.%20E.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Forbes%2C%20J.%20M.%20%282016%29.%20Mapping%20time-course%20mitochondrial%20adaptations%20in%20the%20kidney%20in%20experimental%20diabetes.%20%3Ci%3EClinical%20Science%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E130%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%289%29%2C%20711%26%23x2013%3B720.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1042%5C%2FCS20150838%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1042%5C%2FCS20150838%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Mapping%20time-course%20mitochondrial%20adaptations%20in%20the%20kidney%20in%20experimental%20diabetes%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Melinda%20T.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Coughlan%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Tuong-Vi%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Nguyen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Sally%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Penfold%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Gavin%20C.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Higgins%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Vicki%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Thallas-Bonke%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Sih%20Min%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Tan%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Nicole%20J.%20Van%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Bergen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Karly%20C.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sourris%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Brooke%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Harcourt%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22David%20R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Thorburn%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ian%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Trounce%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mark%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Cooper%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Josephine%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Forbes%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Oxidative%20phosphorylation%20%28OXPHOS%29%20drives%20ATP%20production%20by%20mitochondria%2C%20which%20are%20dynamic%20organelles%2C%20constantly%20fusing%20and%20dividing%20to%20maintain%20kidney%20homoeostasis.%20In%20diabetic%20kidney%20disease%20%28DKD%29%2C%20mitochondria%20appear%20dysfunctional%2C%20but%20the%20temporal%20development%20of%20diabetes-induced%20adaptations%20in%20mitochondrial%20structure%20and%20bioenergetics%20have%20not%20been%20previously%20documented.%20In%20the%20present%20study%2C%20we%20map%20the%20changes%20in%20mitochondrial%20dynamics%20and%20function%20in%20rat%20kidney%20mitochondria%20at%204%2C%208%2C%2016%20and%2032%20weeks%20of%20diabetes.%20Our%20data%20reveal%20that%20changes%20in%20mitochondrial%20bioenergetics%20and%20dynamics%20precede%20the%20development%20of%20albuminuria%20and%20renal%20histological%20changes.%20Specifically%2C%20in%20early%20diabetes%20%284%20weeks%29%2C%20a%20decrease%20in%20ATP%20content%20and%20mitochondrial%20fragmentation%20within%20proximal%20tubule%20epithelial%20cells%20%28PTECs%29%20of%20diabetic%20kidneys%20were%20clearly%20apparent%2C%20but%20no%20changes%20in%20urinary%20albumin%20excretion%20or%20glomerular%20morphology%20were%20evident%20at%20this%20time.%20By%208%20weeks%20of%20diabetes%2C%20there%20was%20increased%20capacity%20for%20mitochondrial%20permeability%20transition%20%28mPT%29%20by%20pore%20opening%2C%20which%20persisted%20over%20time%20and%20correlated%20with%20mitochondrial%20hydrogen%20peroxide%20%28H2O2%29%20generation%20and%20glomerular%20damage.%20Late%20in%20diabetes%2C%20by%20week%2016%2C%20tubular%20damage%20was%20evident%20with%20increased%20urinary%20kidney%20injury%20molecule-1%20%28KIM-1%29%20excretion%2C%20where%20an%20increase%20in%20the%20Complex%20I-linked%20oxygen%20consumption%20rate%20%28OCR%29%2C%20in%20the%20context%20of%20a%20decrease%20in%20kidney%20ATP%2C%20indicated%20mitochondrial%20uncoupling.%20Taken%20together%2C%20these%20data%20show%20that%20changes%20in%20mitochondrial%20bioenergetics%20and%20dynamics%20may%20precede%20the%20development%20of%20the%20renal%20lesion%20in%20diabetes%2C%20and%20this%20supports%20the%20hypothesis%20that%20mitochondrial%20dysfunction%20is%20a%20primary%20cause%20of%20DKD.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222016%5C%2F05%5C%2F01%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1042%5C%2FCS20150838%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220143-5221%2C%201470-8736%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.clinsci.org%5C%2Fcontent%5C%2F130%5C%2F9%5C%2F711%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222016-06-10T19%3A08%3A49Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22WHU2R9PH%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Adamo%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222016%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EAdamo%2C%20R.%20F.%2C%20Fishbein%2C%20I.%2C%20Zhang%2C%20K.%2C%20Wen%2C%20J.%2C%20Levy%2C%20R.%20J.%2C%20Alferiev%2C%20I.%20S.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Chorny%2C%20M.%20%282016%29.%20Magnetically%20enhanced%20cell%20delivery%20for%20accelerating%20recovery%20of%20the%20endothelium%20in%20injured%20arteries.%20%3Ci%3EJournal%20of%20Controlled%20Release%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E222%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20169%26%23x2013%3B175.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.jconrel.2015.12.025%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.jconrel.2015.12.025%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Magnetically%20enhanced%20cell%20delivery%20for%20accelerating%20recovery%20of%20the%20endothelium%20in%20injured%20arteries%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Richard%20F.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Adamo%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ilia%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fishbein%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kehan%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Zhang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Justin%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Robert%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Levy%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ivan%20S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Alferiev%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Michael%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Chorny%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2201%5C%2F2016%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.jconrel.2015.12.025%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2201683659%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0168365915302777%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-12-31T19%3A10%3A51Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22EUVQTK9R%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Falendysz%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015-10-30%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EFalendysz%2C%20E.%20A.%2C%20Lopera%2C%20J.%20G.%2C%20Lorenzsonn%2C%20F.%2C%20Salzer%2C%20J.%20S.%2C%20Hutson%2C%20C.%20L.%2C%20Doty%2C%20J.%2C%20Gallardo-Romero%2C%20N.%2C%20Carroll%2C%20D.%20S.%2C%20Osorio%2C%20J.%20E.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Rocke%2C%20T.%20E.%20%282015%29.%20Further%20Assessment%20of%20Monkeypox%20Virus%20Infection%20in%20Gambian%20Pouched%20Rats%20%28Cricetomys%20gambianus%29%20Using%20In%20Vivo%20Bioluminescent%20Imaging.%20%3Ci%3EPLOS%20Neglected%20Tropical%20Diseases%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E9%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2810%29%2C%20e0004130.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pntd.0004130%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pntd.0004130%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Further%20Assessment%20of%20Monkeypox%20Virus%20Infection%20in%20Gambian%20Pouched%20Rats%20%28Cricetomys%20gambianus%29%20Using%20In%20Vivo%20Bioluminescent%20Imaging%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Elizabeth%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Falendysz%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Juan%20G.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lopera%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Faye%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lorenzsonn%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Johanna%20S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Salzer%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Christina%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hutson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jeffrey%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Doty%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Nadia%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Gallardo-Romero%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Darin%20S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Carroll%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jorge%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Osorio%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Tonie%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Rocke%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%20Desiree%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22LaBeaud%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222015-10-30%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pntd.0004130%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221935-2735%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdx.plos.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pntd.0004130%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-12-31T20%3A36%3A31Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22AE8Z6UCD%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Rosen%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015-09-07%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3ERosen%2C%20D.%20A.%2C%20Hilliard%2C%20J.%20K.%2C%20Tiemann%2C%20K.%20M.%2C%20Todd%2C%20E.%20M.%2C%20Morley%2C%20S.%20C.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Hunstad%2C%20D.%20A.%20%282015%29.%20%3Ci%3EKlebsiella%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%20%3Ci%3Epneumoniae%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%20FimK%20Promotes%20Virulence%20in%20Murine%20Pneumonia.%20%3Ci%3EJournal%20of%20Infectious%20Diseases%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20jiv440.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Finfdis%5C%2Fjiv440%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Finfdis%5C%2Fjiv440%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22%3Ci%3EKlebsiella%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%20%3Ci%3Epneumoniae%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%20FimK%20Promotes%20Virulence%20in%20Murine%20Pneumonia%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22David%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Rosen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Julia%20K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hilliard%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kristin%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Tiemann%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Elizabeth%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Todd%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22S.%20Celeste%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Morley%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22David%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hunstad%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222015-09-07%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1093%5C%2Finfdis%5C%2Fjiv440%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220022-1899%2C%201537-6613%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fjid.oxfordjournals.org%5C%2Flookup%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Finfdis%5C%2Fjiv440%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-12-30T17%3A05%3A32Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22NE7SWIU4%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Danan-Gotthold%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015-05-26%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EDanan-Gotthold%2C%20M.%2C%20Golan-Gerstl%2C%20R.%2C%20Eisenberg%2C%20E.%2C%20Meir%2C%20K.%2C%20Karni%2C%20R.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Levanon%2C%20E.%20Y.%20%282015%29.%20Identification%20of%20recurrent%20regulated%20alternative%20splicing%20events%20across%20human%20solid%20tumors.%20%3Ci%3ENucleic%20Acids%20Research%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E43%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2810%29%2C%205130%26%23x2013%3B5144.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fnar%5C%2Fgkv210%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fnar%5C%2Fgkv210%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Identification%20of%20recurrent%20regulated%20alternative%20splicing%20events%20across%20human%20solid%20tumors%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Danan-Gotthold%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Golan-Gerstl%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Eisenberg%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Meir%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Karni%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22E.%20Y.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Levanon%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222015-05-26%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1093%5C%2Fnar%5C%2Fgkv210%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220305-1048%2C%201362-4962%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fnar.oxfordjournals.org%5C%2Flookup%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fnar%5C%2Fgkv210%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-08-19T17%3A20%3A16Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22HXS8NH3E%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Gao%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015-01-01%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EGao%2C%20X.%2C%20Yang%2C%20T.%2C%20Liu%2C%20M.%2C%20Peleli%2C%20M.%2C%20Zollbrecht%2C%20C.%2C%20Weitzberg%2C%20E.%2C%20Lundberg%2C%20J.%20O.%2C%20Persson%2C%20A.%20E.%20G.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Carlstrom%2C%20M.%20%282015%29.%20NADPH%20Oxidase%20in%20the%20Renal%20Microvasculature%20Is%20a%20Primary%20Target%20for%20Blood%20Pressure-Lowering%20Effects%20by%20Inorganic%20Nitrate%20and%20Nitrite.%20%3Ci%3EHypertension%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E65%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%281%29%2C%20161%26%23x2013%3B170.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1161%5C%2FHYPERTENSIONAHA.114.04222%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1161%5C%2FHYPERTENSIONAHA.114.04222%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22NADPH%20Oxidase%20in%20the%20Renal%20Microvasculature%20Is%20a%20Primary%20Target%20for%20Blood%20Pressure-Lowering%20Effects%20by%20Inorganic%20Nitrate%20and%20Nitrite%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22X.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Gao%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22T.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Yang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Liu%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Peleli%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22C.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Zollbrecht%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Weitzberg%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%20O.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lundberg%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%20E.%20G.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Persson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Carlstrom%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222015-01-01%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1161%5C%2FHYPERTENSIONAHA.114.04222%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220194-911X%2C%201524-4563%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fhyper.ahajournals.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1161%5C%2FHYPERTENSIONAHA.114.04222%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-08-03T15%3A03%3A05Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22NUGCIXQF%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Doldur-Balli%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EDoldur-Balli%2C%20F.%2C%20Ozel%2C%20M.%20N.%2C%20Gulsuner%2C%20S.%2C%20Tekinay%2C%20A.%20B.%2C%20Ozcelik%2C%20T.%2C%20Konu%2C%20O.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Adams%2C%20M.%20M.%20%282015%29.%20Characterization%20of%20a%20novel%20zebrafish%20%28Danio%20rerio%29%20gene%2C%20wdr81%2C%20associated%20with%20cerebellar%20ataxia%2C%20mental%20retardation%20and%20dysequilibrium%20syndrome%20%28CAMRQ%29.%20%3Ci%3EBMC%20Neuroscience%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E16%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%281%29.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1186%5C%2Fs12868-015-0229-4%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1186%5C%2Fs12868-015-0229-4%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Characterization%20of%20a%20novel%20zebrafish%20%28Danio%20rerio%29%20gene%2C%20wdr81%2C%20associated%20with%20cerebellar%20ataxia%2C%20mental%20retardation%20and%20dysequilibrium%20syndrome%20%28CAMRQ%29%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Fusun%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Doldur-Balli%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mehmet%20Neset%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ozel%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Suleyman%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Gulsuner%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ayse%20B.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Tekinay%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Tayfun%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ozcelik%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ozlen%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Konu%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Michelle%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Adams%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2212%5C%2F2015%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1186%5C%2Fs12868-015-0229-4%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221471-2202%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.biomedcentral.com%5C%2F1471-2202%5C%2F16%5C%2F96%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-12-30T18%3A54%3A48Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%2223NCPAZD%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Hezel%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EHezel%2C%20M.%20P.%2C%20Liu%2C%20M.%2C%20Schiffer%2C%20T.%20A.%2C%20Larsen%2C%20F.%20J.%2C%20Checa%2C%20A.%2C%20Wheelock%2C%20C.%20E.%2C%20Carlstr%26%23xF6%3Bm%2C%20M.%2C%20Lundberg%2C%20J.%20O.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Weitzberg%2C%20E.%20%282015%29.%20Effects%20of%20long-term%20dietary%20nitrate%20supplementation%20in%20mice.%20%3Ci%3ERedox%20Biology%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E5%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20234%26%23x2013%3B242.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.redox.2015.05.004%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.redox.2015.05.004%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Effects%20of%20long-term%20dietary%20nitrate%20supplementation%20in%20mice%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Michael%20P.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hezel%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ming%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Liu%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Tomas%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Schiffer%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Filip%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Larsen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Antonio%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Checa%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Craig%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wheelock%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mattias%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Carlstr%5Cu00f6m%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jon%20O.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lundberg%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Eddie%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Weitzberg%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2208%5C%2F2015%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.redox.2015.05.004%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2222132317%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS2213231715000476%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-12-31T18%3A36%3A24Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22W8C3GMRX%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Mootz%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EMootz%2C%20J.%20M.%2C%20Benson%2C%20M.%20A.%2C%20Heim%2C%20C.%20E.%2C%20Crosby%2C%20H.%20A.%2C%20Kavanaugh%2C%20J.%20S.%2C%20Dunman%2C%20P.%20M.%2C%20Kielian%2C%20T.%2C%20Torres%2C%20V.%20J.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Horswill%2C%20A.%20R.%20%282015%29.%20Rot%20is%20a%20key%20regulator%20of%20%3Ci%3EStaphylococcus%20aureus%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%20biofilm%20formation%3A%20Rot%20regulates%20%3Ci%3ES%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%20%3Ci%3E.%20aureus%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%20biofilm%20formation.%20%3Ci%3EMolecular%20Microbiology%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E96%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%282%29%2C%20388%26%23x2013%3B404.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fmmi.12943%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fmmi.12943%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Rot%20is%20a%20key%20regulator%20of%20%3Ci%3EStaphylococcus%20aureus%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%20biofilm%20formation%3A%20Rot%20regulates%20%3Ci%3ES%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%20%3Ci%3E.%20aureus%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%20biofilm%20formation%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Joe%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Mootz%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Meredith%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Benson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Cortney%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Heim%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Heidi%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Crosby%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jeffrey%20S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kavanaugh%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Paul%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Dunman%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Tammy%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kielian%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Victor%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Torres%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Alexander%20R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Horswill%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2204%5C%2F2015%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1111%5C%2Fmmi.12943%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220950382X%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.wiley.com%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fmmi.12943%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222016-01-11T20%3A28%3A45Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22PBZ6XXXM%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Kantharidis%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EKantharidis%2C%20P.%2C%20Hagiwara%2C%20S.%2C%20Brennan%2C%20E.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20McClelland%2C%20A.%20D.%20%282015%29.%20Study%20of%20microRNA%20in%20diabetic%20nephropathy%3A%20Isolation%2C%20quantification%20and%20biological%20function%3A%20MicroRNA%20in%20diabetic%20nephropathy.%20%3Ci%3ENephrology%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E20%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%283%29%2C%20132%26%23x2013%3B139.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fnep.12374%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fnep.12374%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Study%20of%20microRNA%20in%20diabetic%20nephropathy%3A%20Isolation%2C%20quantification%20and%20biological%20function%3A%20MicroRNA%20in%20diabetic%20nephropathy%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Phillip%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kantharidis%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Shinji%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hagiwara%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Eoin%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Brennan%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Aaron%20D.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22McClelland%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2203%5C%2F2015%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1111%5C%2Fnep.12374%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2213205358%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.wiley.com%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fnep.12374%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-31T17%3A19%3A52Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22VUMRWEAW%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Eriksson%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EEriksson%2C%20A.%2C%20Williams%2C%20M.%20J.%2C%20Voisin%2C%20S.%2C%20Hansson%2C%20I.%2C%20Krishnan%2C%20A.%2C%20Philippot%2C%20G.%2C%20Yamskova%2C%20O.%2C%20Herisson%2C%20F.%20M.%2C%20Dnyansagar%2C%20R.%2C%20Moschonis%2C%20G.%2C%20Manios%2C%20Y.%2C%20Chrousos%2C%20G.%20P.%2C%20Olszewski%2C%20P.%20K.%2C%20Frediksson%2C%20R.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Schi%26%23xF6%3Bth%2C%20H.%20B.%20%282015%29.%20Implication%20of%20coronin%207%20in%20body%20weight%20regulation%20in%20humans%2C%20mice%20and%20flies.%20%3Ci%3EBMC%20Neuroscience%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E16%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%281%29%2C%2013.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1186%5C%2Fs12868-015-0151-9%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1186%5C%2Fs12868-015-0151-9%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Implication%20of%20coronin%207%20in%20body%20weight%20regulation%20in%20humans%2C%20mice%20and%20flies%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Anders%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Eriksson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Michael%20J%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Williams%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Sarah%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Voisin%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ida%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hansson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Arunkumar%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Krishnan%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Gaetan%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Philippot%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Olga%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Yamskova%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Florence%20M%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Herisson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Rohit%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Dnyansagar%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22George%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Moschonis%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Yannis%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Manios%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22George%20P%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Chrousos%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Pawel%20K%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Olszewski%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Robert%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Frediksson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Helgi%20B%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Schi%5Cu00f6th%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1186%5C%2Fs12868-015-0151-9%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221471-2202%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.biomedcentral.com%5C%2F1471-2202%5C%2F16%5C%2F13%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-12-31T20%3A09%3A52Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%227EWWE2E8%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Zhang%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EZhang%2C%20Z.%2C%20He%2C%20L.%2C%20Hu%2C%20S.%2C%20Wang%2C%20Y.%2C%20Lai%2C%20Q.%2C%20Yang%2C%20P.%2C%20Yu%2C%20Q.%2C%20Zhang%2C%20S.%2C%20Xiong%2C%20F.%2C%20Simsekyilmaz%2C%20S.%2C%20Ning%2C%20Q.%2C%20Li%2C%20J.%2C%20Zhang%2C%20D.%2C%20Zhang%2C%20H.%2C%20Xiang%2C%20X.%2C%20Zhou%2C%20Z.%2C%20Sun%2C%20H.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Wang%2C%20C.-Y.%20%282015%29.%20AAL%20exacerbates%20pro-inflammatory%20response%20in%20macrophages%20by%20regulating%20Mincle%5C%2FSyk%5C%2FCard9%20signaling%20along%20with%20the%20Nlrp3%20inflammasome%20assembly.%20%3Ci%3EAmerican%20Journal%20of%20Translational%20Research%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E7%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2810%29%2C%201812%26%23x2013%3B1825.%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22AAL%20exacerbates%20pro-inflammatory%20response%20in%20macrophages%20by%20regulating%20Mincle%5C%2FSyk%5C%2FCard9%20signaling%20along%20with%20the%20Nlrp3%20inflammasome%20assembly%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Zhijun%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Zhang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Long%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22He%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Shuang%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hu%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Yi%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Qiaohong%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lai%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ping%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Yang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Qilin%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Yu%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Shu%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Zhang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Fei%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Xiong%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Sakine%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Simsekyilmaz%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Qin%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ning%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jinxiu%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Li%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Dongshan%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Zhang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Hongliang%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Zhang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Xudong%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Xiang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Zhiguang%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Zhou%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Hui%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sun%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Cong-Yi%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wang%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%22%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%22%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-12-30T20%3A03%3A39Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22SBSRG4SI%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Hains%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014-10-01%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EHains%2C%20D.%20S.%2C%20Chen%2C%20X.%2C%20Saxena%2C%20V.%2C%20Barr-Beare%2C%20E.%2C%20Flemming%2C%20W.%2C%20Easterling%2C%20R.%2C%20Becknell%2C%20B.%2C%20Schwartz%2C%20G.%20J.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Schwaderer%2C%20A.%20L.%20%282014%29.%20Carbonic%20anhydrase%202%20deficiency%20leads%20to%20increased%20pyelonephritis%20susceptibility.%20%3Ci%3EAJP%3A%20Renal%20Physiology%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E307%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%287%29%2C%20F869%26%23x2013%3BF880.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1152%5C%2Fajprenal.00344.2014%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1152%5C%2Fajprenal.00344.2014%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Carbonic%20anhydrase%202%20deficiency%20leads%20to%20increased%20pyelonephritis%20susceptibility%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22D.%20S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hains%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22X.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Chen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22V.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Saxena%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Barr-Beare%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22W.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Flemming%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Easterling%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22B.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Becknell%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22G.%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Schwartz%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Schwaderer%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222014-10-01%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1152%5C%2Fajprenal.00344.2014%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221931-857X%2C%201522-1466%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fajprenal.physiology.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1152%5C%2Fajprenal.00344.2014%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-08-03T16%3A00%3A47Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%226X5P59RJ%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22van%20der%20Plas-Duivesteijn%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014-03-07%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3Evan%20der%20Plas-Duivesteijn%2C%20S.%20J.%2C%20Mohammed%2C%20Y.%2C%20Dalebout%2C%20H.%2C%20Meijer%2C%20A.%2C%20Botermans%2C%20A.%2C%20Hoogendijk%2C%20J.%20L.%2C%20Henneman%2C%20A.%20A.%2C%20Deelder%2C%20A.%20M.%2C%20Spaink%2C%20H.%20P.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Palmblad%2C%20M.%20%282014%29.%20Identifying%20Proteins%20in%20Zebrafish%20Embryos%20Using%20Spectral%20Libraries%20Generated%20from%20Dissected%20Adult%20Organs%20and%20Tissues.%20%3Ci%3EJournal%20of%20Proteome%20Research%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E13%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%283%29%2C%201537%26%23x2013%3B1544.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1021%5C%2Fpr4010585%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1021%5C%2Fpr4010585%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Identifying%20Proteins%20in%20Zebrafish%20Embryos%20Using%20Spectral%20Libraries%20Generated%20from%20Dissected%20Adult%20Organs%20and%20Tissues%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Suzanne%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22van%20der%20Plas-Duivesteijn%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Yassene%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Mohammed%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Hans%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Dalebout%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Annemarie%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Meijer%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Anouk%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Botermans%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jordy%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hoogendijk%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Alex%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Henneman%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Andr%5Cu00e9%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Deelder%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Herman%20P.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Spaink%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Magnus%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Palmblad%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222014-03-07%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1021%5C%2Fpr4010585%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221535-3893%2C%201535-3907%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fpubs.acs.org%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2Fabs%5C%2F10.1021%5C%2Fpr4010585%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-08-10T16%3A33%3A28Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%225NWGEHBC%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Wang%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EWang%2C%20Z.%2C%20Wei%2C%20M.%2C%20Wang%2C%20M.%2C%20Chen%2C%20L.%2C%20Liu%2C%20H.%2C%20Ren%2C%20Y.%2C%20Shi%2C%20K.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Jiang%2C%20H.%20%282014%29.%20Inhibition%20of%20Macrophage%20Migration%20Inhibitory%20Factor%20Reduces%20Diabetic%20Nephropathy%20in%20Type%20II%20Diabetes%20Mice.%20%3Ci%3EInflammation%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E37%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%286%29%2C%202020%26%23x2013%3B2029.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1007%5C%2Fs10753-014-9934-x%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1007%5C%2Fs10753-014-9934-x%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Inhibition%20of%20Macrophage%20Migration%20Inhibitory%20Factor%20Reduces%20Diabetic%20Nephropathy%20in%20Type%20II%20Diabetes%20Mice%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Zhigang%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Meng%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wei%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Meng%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Lei%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Chen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Hua%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Liu%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Yi%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ren%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kehui%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Shi%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Hongli%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Jiang%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2212%5C%2F2014%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1007%5C%2Fs10753-014-9934-x%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220360-3997%2C%201573-2576%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flink.springer.com%5C%2F10.1007%5C%2Fs10753-014-9934-x%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222016-01-12T16%3A28%3A06Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22IN27G8I6%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Huang%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EHuang%2C%20C.-C.%2C%20Lou%2C%20B.-S.%2C%20Hsu%2C%20F.-L.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Hou%2C%20C.-C.%20%282014%29.%20Use%20of%20urinary%20metabolomics%20to%20evaluate%20the%20effect%20of%20hyperuricemia%20on%20the%20kidney.%20%3Ci%3EFood%20and%20Chemical%20Toxicology%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E74%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%2035%26%23x2013%3B44.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.fct.2014.08.017%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.fct.2014.08.017%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Use%20of%20urinary%20metabolomics%20to%20evaluate%20the%20effect%20of%20hyperuricemia%20on%20the%20kidney%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Chi-Chang%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Huang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Bih-Show%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lou%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Feng-Lin%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hsu%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Chia-Chung%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hou%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2212%5C%2F2014%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.fct.2014.08.017%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2202786915%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0278691514003986%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-08-18T16%3A35%3A00Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22X9F9E8BR%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Borschensky%20and%20Reinacher%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EBorschensky%2C%20C.%20M.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Reinacher%2C%20M.%20%282014%29.%20Mutations%20in%20the%203c%20and%207b%20genes%20of%20feline%20coronavirus%20in%20spontaneously%20affected%20FIP%20cats.%20%3Ci%3EResearch%20in%20Veterinary%20Science%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E97%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%282%29%2C%20333%26%23x2013%3B340.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.rvsc.2014.07.016%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.rvsc.2014.07.016%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Mutations%20in%20the%203c%20and%207b%20genes%20of%20feline%20coronavirus%20in%20spontaneously%20affected%20FIP%20cats%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22C.M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Borschensky%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Reinacher%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2210%5C%2F2014%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.rvsc.2014.07.016%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2200345288%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0034528814002185%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-10-30T19%3A39%3A51Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%224TZE3UNM%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Parra%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EParra%2C%20S.%2C%20Huang%2C%20X.%2C%20Charbeneau%2C%20R.%20A.%2C%20Wade%2C%20S.%20M.%2C%20Kaur%2C%20K.%2C%20Rorabaugh%2C%20B.%20R.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Neubig%2C%20R.%20R.%20%282014%29.%20Conditional%20disruption%20of%20interactions%20between%20G%26%23x3B1%3Bi2%20and%20regulator%20of%20G%20protein%20signaling%20%28RGS%29%20proteins%20protects%20the%20heart%20from%20ischemic%20injury.%20%3Ci%3EBMC%20Pharmacology%20and%20Toxicology%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E15%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%281%29%2C%2029.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1186%5C%2F2050-6511-15-29%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1186%5C%2F2050-6511-15-29%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Conditional%20disruption%20of%20interactions%20between%20G%5Cu03b1i2%20and%20regulator%20of%20G%20protein%20signaling%20%28RGS%29%20proteins%20protects%20the%20heart%20from%20ischemic%20injury%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Sergio%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Parra%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Xinyan%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Huang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Raelene%20A%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Charbeneau%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Susan%20M%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wade%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kuljeet%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kaur%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Boyd%20R%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Rorabaugh%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Richard%20R%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Neubig%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222014%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1186%5C%2F2050-6511-15-29%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%222050-6511%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.biomedcentral.com%5C%2F2050-6511%5C%2F15%5C%2F29%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222016-01-13T20%3A59%3A02Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22CG63U65K%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Melero%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EMelero%2C%20M.%2C%20Garc%26%23xED%3Ba-P%26%23xE1%3Brraga%2C%20D.%2C%20Corpa%2C%20J.%2C%20Ortega%2C%20J.%2C%20Rubio-Guerri%2C%20C.%2C%20Crespo%2C%20J.%2C%20Rivera-Arroyo%2C%20B.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20S%26%23xE1%3Bnchez-Vizca%26%23xED%3Bno%2C%20J.%20%282014%29.%20First%20molecular%20detection%20and%20characterization%20of%20herpesvirus%20and%20poxvirus%20in%20a%20Pacific%20walrus%20%28Odobenus%20rosmarus%20divergens%29.%20%3Ci%3EBMC%20Veterinary%20Research%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E10%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%281%29%2C%20968.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1186%5C%2Fs12917-014-0308-2%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1186%5C%2Fs12917-014-0308-2%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22First%20molecular%20detection%20and%20characterization%20of%20herpesvirus%20and%20poxvirus%20in%20a%20Pacific%20walrus%20%28Odobenus%20rosmarus%20divergens%29%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mar%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Melero%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Daniel%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Garc%5Cu00eda-P%5Cu00e1rraga%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Juan%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Corpa%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Joaqu%5Cu00edn%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ortega%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Consuelo%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Rubio-Guerri%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jos%5Cu00e9%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Crespo%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Bel%5Cu00e9n%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Rivera-Arroyo%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jos%5Cu00e9%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22S%5Cu00e1nchez-Vizca%5Cu00edno%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222014%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1186%5C%2Fs12917-014-0308-2%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221746-6148%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.biomedcentral.com%5C%2F1746-6148%5C%2F10%5C%2F968%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222016-01-12T17%3A25%3A07Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22QNPPN824%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Becknell%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013-10-21%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EBecknell%2C%20B.%2C%20Spencer%2C%20J.%20D.%2C%20Carpenter%2C%20A.%20R.%2C%20Chen%2C%20X.%2C%20Singh%2C%20A.%2C%20Ploeger%2C%20S.%2C%20Kline%2C%20J.%2C%20Ellsworth%2C%20P.%2C%20Li%2C%20B.%2C%20Proksch%2C%20E.%2C%20Schwaderer%2C%20A.%20L.%2C%20Hains%2C%20D.%20S.%2C%20Justice%2C%20S.%20S.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20McHugh%2C%20K.%20M.%20%282013%29.%20Expression%20and%20Antimicrobial%20Function%20of%20Beta-Defensin%201%20in%20the%20Lower%20Urinary%20Tract.%20%3Ci%3EPLoS%20ONE%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E8%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2810%29%2C%20e77714.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0077714%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0077714%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Expression%20and%20Antimicrobial%20Function%20of%20Beta-Defensin%201%20in%20the%20Lower%20Urinary%20Tract%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Brian%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Becknell%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22John%20David%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Spencer%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ashley%20R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Carpenter%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Xi%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Chen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Aspinder%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Singh%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Suzanne%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ploeger%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jennifer%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kline%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Patrick%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ellsworth%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Birong%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Li%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ehrhardt%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Proksch%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Andrew%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Schwaderer%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22David%20S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hains%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Sheryl%20S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Justice%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kirk%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22McHugh%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Olivier%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Neyrolles%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013-10-21%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0077714%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221932-6203%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdx.plos.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0077714%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-20T15%3A44%3A53Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%225ZPHANX4%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Cheng%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013-10-11%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3ECheng%2C%20X.%2C%20Guo%2C%20S.%2C%20Liu%2C%20Y.%2C%20Chu%2C%20H.%2C%20Hakimi%2C%20P.%2C%20Berger%2C%20N.%20A.%2C%20Hanson%2C%20R.%20W.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Kao%2C%20H.-Y.%20%282013%29.%20Ablation%20of%20Promyelocytic%20Leukemia%20Protein%20%28PML%29%20Re-patterns%20Energy%20Balance%20and%20Protects%20Mice%20from%20Obesity%20Induced%20by%20a%20Western%20Diet.%20%3Ci%3EJournal%20of%20Biological%20Chemistry%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E288%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2841%29%2C%2029746%26%23x2013%3B29759.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1074%5C%2Fjbc.M113.487595%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1074%5C%2Fjbc.M113.487595%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Ablation%20of%20Promyelocytic%20Leukemia%20Protein%20%28PML%29%20Re-patterns%20Energy%20Balance%20and%20Protects%20Mice%20from%20Obesity%20Induced%20by%20a%20Western%20Diet%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22X.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Cheng%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Guo%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Y.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Liu%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22H.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Chu%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22P.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hakimi%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22N.%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Berger%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22R.%20W.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hanson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22H.-Y.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kao%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013-10-11%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1074%5C%2Fjbc.M113.487595%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220021-9258%2C%201083-351X%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.jbc.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1074%5C%2Fjbc.M113.487595%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-20T16%3A09%3A49Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22ISH32D5C%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Karauzum%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013-06-07%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EKarauzum%2C%20H.%2C%20Adhikari%2C%20R.%20P.%2C%20Sarwar%2C%20J.%2C%20Devi%2C%20V.%20S.%2C%20Abaandou%2C%20L.%2C%20Haudenschild%2C%20C.%2C%20Mahmoudieh%2C%20M.%2C%20Boroun%2C%20A.%20R.%2C%20Vu%2C%20H.%2C%20Nguyen%2C%20T.%2C%20Warfield%2C%20K.%20L.%2C%20Shulenin%2C%20S.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Aman%2C%20M.%20J.%20%282013%29.%20Structurally%20Designed%20Attenuated%20Subunit%20Vaccines%20for%20S.%20aureus%20LukS-PV%20and%20LukF-PV%20Confer%20Protection%20in%20a%20Mouse%20Bacteremia%20Model.%20%3Ci%3EPLoS%20ONE%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E8%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%286%29%2C%20e65384.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0065384%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0065384%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Structurally%20Designed%20Attenuated%20Subunit%20Vaccines%20for%20S.%20aureus%20LukS-PV%20and%20LukF-PV%20Confer%20Protection%20in%20a%20Mouse%20Bacteremia%20Model%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Hatice%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Karauzum%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Rajan%20P.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Adhikari%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jawad%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sarwar%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22V.%20Sathya%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Devi%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Laura%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Abaandou%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Christian%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Haudenschild%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mahta%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Mahmoudieh%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Atefeh%20R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Boroun%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Hong%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Vu%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Tam%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Nguyen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kelly%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Warfield%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Sergey%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Shulenin%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%20Javad%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Aman%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Dipshikha%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Chakravortty%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013-6-7%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0065384%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221932-6203%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdx.plos.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0065384%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-20T17%3A21%3A51Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22UZQFBRF9%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Nakayama%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013-05-22%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3ENakayama%2C%20K.%20H.%2C%20Lee%2C%20C.%20C.%20I.%2C%20Batchelder%2C%20C.%20A.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Tarantal%2C%20A.%20F.%20%282013%29.%20Tissue%20Specificity%20of%20Decellularized%20Rhesus%20Monkey%20Kidney%20and%20Lung%20Scaffolds.%20%3Ci%3EPLoS%20ONE%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E8%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%285%29%2C%20e64134.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0064134%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0064134%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Tissue%20Specificity%20of%20Decellularized%20Rhesus%20Monkey%20Kidney%20and%20Lung%20Scaffolds%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Karina%20H.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Nakayama%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22C.%20Chang%20I.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lee%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Cynthia%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Batchelder%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Alice%20F.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Tarantal%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Junming%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Yue%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013-5-22%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0064134%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221932-6203%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdx.plos.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0064134%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-10T14%3A52%3A07Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22E57IW7UW%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Hoang%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013-01-31%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EHoang%2C%20H.%20D.%2C%20Prasain%2C%20J.%20K.%2C%20Dorand%2C%20D.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Miller%2C%20M.%20A.%20%282013%29.%20A%20Heterogeneous%20Mixture%20of%20F-Series%20Prostaglandins%20Promotes%20Sperm%20Guidance%20in%20the%20Caenorhabditis%20elegans%20Reproductive%20Tract.%20%3Ci%3EPLoS%20Genetics%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E9%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%281%29%2C%20e1003271.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pgen.1003271%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pgen.1003271%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22A%20Heterogeneous%20Mixture%20of%20F-Series%20Prostaglandins%20Promotes%20Sperm%20Guidance%20in%20the%20Caenorhabditis%20elegans%20Reproductive%20Tract%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Hieu%20D.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hoang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jeevan%20K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Prasain%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Dixon%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Dorand%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Michael%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Miller%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kaveh%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ashrafi%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013-1-31%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pgen.1003271%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221553-7404%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdx.plos.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pgen.1003271%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-08T14%3A58%3A51Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22Q28KGFK2%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Carlstr%5Cu00f6m%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3ECarlstr%26%23xF6%3Bm%2C%20M.%2C%20Brown%2C%20R.%20D.%2C%20Yang%2C%20T.%2C%20Hezel%2C%20M.%2C%20Larsson%2C%20E.%2C%20Scheffer%2C%20P.%20G.%2C%20Teerlink%2C%20T.%2C%20Lundberg%2C%20J.%20O.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Persson%2C%20A.%20E.%20G.%20%282013%29.%20L-arginine%20or%20tempol%20supplementation%20improves%20renal%20and%20cardiovascular%20function%20in%20rats%20with%20reduced%20renal%20mass%20and%20chronic%20high%20salt%20intake.%20%3Ci%3EActa%20Physiologica%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E207%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%284%29%2C%20732%26%23x2013%3B741.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fapha.12079%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fapha.12079%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22L-arginine%20or%20tempol%20supplementation%20improves%20renal%20and%20cardiovascular%20function%20in%20rats%20with%20reduced%20renal%20mass%20and%20chronic%20high%20salt%20intake%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Carlstr%5Cu00f6m%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22R.%20D.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Brown%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22T.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Yang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hezel%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Larsson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22P.%20G.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Scheffer%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22T.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Teerlink%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%20O.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lundberg%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%20E.%20G.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Persson%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2204%5C%2F2013%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1111%5C%2Fapha.12079%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2217481708%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.wiley.com%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fapha.12079%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-15T15%3A45%3A48Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22TC63ICA3%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Rubio-Guerri%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3ERubio-Guerri%2C%20C.%2C%20Melero%2C%20M.%2C%20Esper%26%23xF3%3Bn%2C%20F.%2C%20Belli%26%23xE8%3Bre%2C%20E.%2C%20Arbelo%2C%20M.%2C%20Crespo%2C%20J.%2C%20Sierra%2C%20E.%2C%20Garc%26%23xED%3Ba-P%26%23xE1%3Brraga%2C%20D.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20S%26%23xE1%3Bnchez-Vizca%26%23xED%3Bno%2C%20J.%20%282013%29.%20Unusual%20striped%20dolphin%20mass%20mortality%20episode%20related%20to%20cetacean%20morbillivirus%20in%20the%20Spanish%20Mediterranean%20sea.%20%3Ci%3EBMC%20Veterinary%20Research%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E9%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%281%29%2C%20106.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1186%5C%2F1746-6148-9-106%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1186%5C%2F1746-6148-9-106%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Unusual%20striped%20dolphin%20mass%20mortality%20episode%20related%20to%20cetacean%20morbillivirus%20in%20the%20Spanish%20Mediterranean%20sea%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Consuelo%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Rubio-Guerri%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mar%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Melero%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Fernando%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Esper%5Cu00f3n%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Edwige%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Belli%5Cu00e8re%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Manuel%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Arbelo%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jose%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Crespo%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Eva%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sierra%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Daniel%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Garc%5Cu00eda-P%5Cu00e1rraga%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jose%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22S%5Cu00e1nchez-Vizca%5Cu00edno%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1186%5C%2F1746-6148-9-106%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221746-6148%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.biomedcentral.com%5C%2F1746-6148%5C%2F9%5C%2F106%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-13T16%3A20%3A42Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22UV3JU2QE%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Hanstein%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EHanstein%2C%20R.%2C%20Negoro%2C%20H.%2C%20Patel%2C%20N.%20K.%2C%20Charollais%2C%20A.%2C%20Meda%2C%20P.%2C%20Spray%2C%20D.%20C.%2C%20Suadicani%2C%20S.%20O.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Scemes%2C%20E.%20%282013%29.%20Promises%20and%20pitfalls%20of%20a%20Pannexin1%20transgenic%20mouse%20line.%20%3Ci%3EFrontiers%20in%20Pharmacology%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E4%3C%5C%2Fi%3E.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3389%5C%2Ffphar.2013.00061%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3389%5C%2Ffphar.2013.00061%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Promises%20and%20pitfalls%20of%20a%20Pannexin1%20transgenic%20mouse%20line%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Regina%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hanstein%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Hiromitsu%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Negoro%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Naman%20K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Patel%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Anne%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Charollais%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Paolo%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Meda%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22David%20C.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Spray%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Sylvia%20O.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Suadicani%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Eliana%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Scemes%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.3389%5C%2Ffphar.2013.00061%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221663-9812%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fjournal.frontiersin.org%5C%2Farticle%5C%2F10.3389%5C%2Ffphar.2013.00061%5C%2Fabstract%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-20T17%3A15%3A36Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22F9ACZKNR%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Chaker%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EChaker%2C%20B.%2C%20Samra%2C%20T.%20A.%2C%20Datta%2C%20N.%20S.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Abou-Samra%2C%20A.%20B.%20%282013%29.%20Altered%20Responses%20to%20Cold%20Environment%20in%20Urocortin%201%20and%20Corticotropin-Releasing%20Factor%20Deficient%20Mice.%20%3Ci%3EPhysiology%20Journal%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E2013%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%201%26%23x2013%3B7.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1155%5C%2F2013%5C%2F185767%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1155%5C%2F2013%5C%2F185767%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Altered%20Responses%20to%20Cold%20Environment%20in%20Urocortin%201%20and%20Corticotropin-Releasing%20Factor%20Deficient%20Mice%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Bayan%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Chaker%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Tareq%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Samra%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Nabanita%20S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Datta%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Abdul%20B.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Abou-Samra%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1155%5C%2F2013%5C%2F185767%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%222314-4300%2C%202314-4319%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.hindawi.com%5C%2Fjournals%5C%2Fphysiology%5C%2F2013%5C%2F185767%5C%2F%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-20T16%3A06%3A38Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22GUA4RTZR%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Kumar%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222012-08-31%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EKumar%2C%20M.%2C%20Roe%2C%20K.%2C%20Nerurkar%2C%20P.%20V.%2C%20Namekar%2C%20M.%2C%20Orillo%2C%20B.%2C%20Verma%2C%20S.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Nerurkar%2C%20V.%20R.%20%282012%29.%20Impaired%20Virus%20Clearance%2C%20Compromised%20Immune%20Response%20and%20Increased%20Mortality%20in%20Type%202%20Diabetic%20Mice%20Infected%20with%20West%20Nile%20Virus.%20%3Ci%3EPLoS%20ONE%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E7%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%288%29%2C%20e44682.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0044682%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0044682%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Impaired%20Virus%20Clearance%2C%20Compromised%20Immune%20Response%20and%20Increased%20Mortality%20in%20Type%202%20Diabetic%20Mice%20Infected%20with%20West%20Nile%20Virus%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mukesh%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kumar%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kelsey%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Roe%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Pratibha%20V.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Nerurkar%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Madhuri%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Namekar%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Beverly%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Orillo%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Saguna%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Verma%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Vivek%20R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Nerurkar%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Robyn%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Klein%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222012-8-31%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0044682%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221932-6203%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdx.plos.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0044682%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-20T17%3A23%3A53Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%223K4SX5JN%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Hanke%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222012-08-03%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EHanke%2C%20M.%20L.%2C%20Angle%2C%20A.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Kielian%2C%20T.%20%282012%29.%20MyD88-Dependent%20Signaling%20Influences%20Fibrosis%20and%20Alternative%20Macrophage%20Activation%20during%20Staphylococcus%20aureus%20Biofilm%20Infection.%20%3Ci%3EPLoS%20ONE%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E7%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%288%29%2C%20e42476.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0042476%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0042476%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22MyD88-Dependent%20Signaling%20Influences%20Fibrosis%20and%20Alternative%20Macrophage%20Activation%20during%20Staphylococcus%20aureus%20Biofilm%20Infection%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mark%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hanke%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Amanda%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Angle%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Tammy%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kielian%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Dipshikha%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Chakravortty%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222012-8-3%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0042476%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221932-6203%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdx.plos.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0042476%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-20T17%3A13%3A52Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22ZPMRDRZ2%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Adhikari%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222012-06-06%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EAdhikari%2C%20R.%20P.%2C%20Karauzum%2C%20H.%2C%20Sarwar%2C%20J.%2C%20Abaandou%2C%20L.%2C%20Mahmoudieh%2C%20M.%2C%20Boroun%2C%20A.%20R.%2C%20Vu%2C%20H.%2C%20Nguyen%2C%20T.%2C%20Devi%2C%20V.%20S.%2C%20Shulenin%2C%20S.%2C%20Warfield%2C%20K.%20L.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Aman%2C%20M.%20J.%20%282012%29.%20Novel%20Structurally%20Designed%20Vaccine%20for%20S.%20aureus%20%26%23x3B1%3B-Hemolysin%3A%20Protection%20against%20Bacteremia%20and%20Pneumonia.%20%3Ci%3EPLoS%20ONE%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E7%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%286%29%2C%20e38567.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0038567%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0038567%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Novel%20Structurally%20Designed%20Vaccine%20for%20S.%20aureus%20%5Cu03b1-Hemolysin%3A%20Protection%20against%20Bacteremia%20and%20Pneumonia%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Rajan%20P.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Adhikari%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Hatice%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Karauzum%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jawad%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sarwar%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Laura%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Abaandou%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mahta%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Mahmoudieh%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Atefeh%20R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Boroun%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Hong%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Vu%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Tam%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Nguyen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22V.%20Sathya%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Devi%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Sergey%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Shulenin%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kelly%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Warfield%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%20Javad%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Aman%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Michael%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Otto%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222012-6-6%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0038567%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221932-6203%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdx.plos.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0038567%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-20T15%3A31%3A56Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22INDQTUME%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Fox%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222012%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EFox%2C%20K.%20A.%2C%20Longo%2C%20M.%2C%20Tamayo%2C%20E.%2C%20Gamble%2C%20P.%2C%20Makhlouf%2C%20M.%2C%20Mateus%2C%20J.%20F.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Saade%2C%20G.%20R.%20%282012%29.%20Sex-specific%20effects%20of%20nicotine%20exposure%20on%20developmental%20programming%20of%20blood%20pressure%20and%20vascular%20reactivity%20in%20the%20C57Bl%5C%2F6J%20mouse.%20%3Ci%3EAmerican%20Journal%20of%20Obstetrics%20and%20Gynecology%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E207%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%283%29%2C%20208.e1-208.e9.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.ajog.2012.06.021%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.ajog.2012.06.021%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Sex-specific%20effects%20of%20nicotine%20exposure%20on%20developmental%20programming%20of%20blood%20pressure%20and%20vascular%20reactivity%20in%20the%20C57Bl%5C%2F6J%20mouse%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Karin%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fox%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Monica%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Longo%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Esther%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Tamayo%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Phyllis%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Gamble%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Michel%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Makhlouf%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Julio%20F.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Mateus%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22George%20R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Saade%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2209%5C%2F2012%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.ajog.2012.06.021%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2200029378%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0002937812006229%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-20T16%3A35%3A26Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22UR66QNH6%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Harcourt%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222012%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EHarcourt%2C%20B.%20E.%2C%20Forbes%2C%20J.%20M.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Matthews%2C%20V.%20B.%20%282012%29.%20Obesity-induced%20renal%20impairment%20is%20exacerbated%20in%20interleukin-6-knockout%20mice%3A%20IL-6%20KO%20worsens%20kidney%20injury%20in%20obesity.%20%3Ci%3ENephrology%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E17%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%283%29%2C%20257%26%23x2013%3B262.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fj.1440-1797.2011.01547.x%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fj.1440-1797.2011.01547.x%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Obesity-induced%20renal%20impairment%20is%20exacerbated%20in%20interleukin-6-knockout%20mice%3A%20IL-6%20KO%20worsens%20kidney%20injury%20in%20obesity%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Brooke%20E%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Harcourt%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Josephine%20M%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Forbes%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Vance%20B%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Matthews%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2203%5C%2F2012%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1111%5C%2Fj.1440-1797.2011.01547.x%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2213205358%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.wiley.com%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fj.1440-1797.2011.01547.x%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-16T17%3A55%3A01Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22U8QVV6VD%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Carlstrom%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222011-02-15%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3ECarlstrom%2C%20M.%2C%20Persson%2C%20A.%20E.%20G.%2C%20Larsson%2C%20E.%2C%20Hezel%2C%20M.%2C%20Scheffer%2C%20P.%20G.%2C%20Teerlink%2C%20T.%2C%20Weitzberg%2C%20E.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Lundberg%2C%20J.%20O.%20%282011%29.%20Dietary%20nitrate%20attenuates%20oxidative%20stress%2C%20prevents%20cardiac%20and%20renal%20injuries%2C%20and%20reduces%20blood%20pressure%20in%20salt-induced%20hypertension.%20%3Ci%3ECardiovascular%20Research%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E89%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%283%29%2C%20574%26%23x2013%3B585.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fcvr%5C%2Fcvq366%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fcvr%5C%2Fcvq366%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Dietary%20nitrate%20attenuates%20oxidative%20stress%2C%20prevents%20cardiac%20and%20renal%20injuries%2C%20and%20reduces%20blood%20pressure%20in%20salt-induced%20hypertension%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Carlstrom%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%20E.%20G.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Persson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Larsson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hezel%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22P.%20G.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Scheffer%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22T.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Teerlink%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Weitzberg%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%20O.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lundberg%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222011-02-15%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1093%5C%2Fcvr%5C%2Fcvq366%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220008-6363%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fcardiovascres.oxfordjournals.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fcvr%5C%2Fcvq366%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-23T15%3A06%3A07Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22S32T26M4%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Fox%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222011%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EFox%2C%20K.%20A.%2C%20Longo%2C%20M.%2C%20Tamayo%2C%20E.%2C%20Kechichian%2C%20T.%2C%20Bytautiene%2C%20E.%2C%20Hankins%2C%20G.%20D.%20V.%2C%20Saade%2C%20G.%20R.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Costantine%2C%20M.%20M.%20%282011%29.%20Effects%20of%20pravastatin%20on%20mediators%20of%20vascular%20function%20in%20a%20mouse%20model%20of%20soluble%20Fms-like%20tyrosine%20kinase-1%26%23x2013%3Binduced%20preeclampsia.%20%3Ci%3EAmerican%20Journal%20of%20Obstetrics%20and%20Gynecology%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E205%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%284%29%2C%20366.e1-366.e5.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.ajog.2011.06.083%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.ajog.2011.06.083%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Effects%20of%20pravastatin%20on%20mediators%20of%20vascular%20function%20in%20a%20mouse%20model%20of%20soluble%20Fms-like%20tyrosine%20kinase-1%5Cu2013induced%20preeclampsia%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Karin%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fox%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Monica%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Longo%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Esther%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Tamayo%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Talar%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kechichian%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Egle%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Bytautiene%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Gary%20D.V.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hankins%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22George%20R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Saade%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Maged%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Costantine%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2210%5C%2F2011%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.ajog.2011.06.083%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2200029378%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0002937811008313%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-23T16%3A58%3A26Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22SXKW2ZNV%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Thai%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222010-08-05%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EThai%2C%20K.%20H.%2C%20Thathireddy%2C%20A.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Hsieh%2C%20M.%20H.%20%282010%29.%20Transurethral%20Induction%20of%20Mouse%20Urinary%20Tract%20Infection.%20%3Ci%3EJournal%20of%20Visualized%20Experiments%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E42%3C%5C%2Fi%3E.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3791%5C%2F2070%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3791%5C%2F2070%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Transurethral%20Induction%20of%20Mouse%20Urinary%20Tract%20Infection%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kim%20H.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Thai%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Anuradha%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Thathireddy%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Michael%20H.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hsieh%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222010-8-5%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.3791%5C%2F2070%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221940-087X%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.jove.com%5C%2Findex%5C%2FDetails.stp%3FID%3D2070%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-22T14%3A26%3A35Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22EVHFA7JI%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Rayner%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222010-06-18%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3ERayner%2C%20K.%20J.%2C%20Suarez%2C%20Y.%2C%20Davalos%2C%20A.%2C%20Parathath%2C%20S.%2C%20Fitzgerald%2C%20M.%20L.%2C%20Tamehiro%2C%20N.%2C%20Fisher%2C%20E.%20A.%2C%20Moore%2C%20K.%20J.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Fernandez-Hernando%2C%20C.%20%282010%29.%20MiR-33%20Contributes%20to%20the%20Regulation%20of%20Cholesterol%20Homeostasis.%20%3Ci%3EScience%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E328%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%285985%29%2C%201570%26%23x2013%3B1573.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1126%5C%2Fscience.1189862%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1126%5C%2Fscience.1189862%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22MiR-33%20Contributes%20to%20the%20Regulation%20of%20Cholesterol%20Homeostasis%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22K.%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Rayner%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Y.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Suarez%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Davalos%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Parathath%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fitzgerald%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22N.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Tamehiro%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22E.%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fisher%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22K.%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Moore%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22C.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fernandez-Hernando%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222010-06-18%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1126%5C%2Fscience.1189862%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220036-8075%2C%201095-9203%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.sciencemag.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1126%5C%2Fscience.1189862%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-27T14%3A34%3A20Z%22%7D%7D%5D%7D
Coughlan, M. T., Nguyen, T.-V., Penfold, S. A., Higgins, G. C., Thallas-Bonke, V., Tan, S. M., Bergen, N. J. V., Sourris, K. C., Harcourt, B. E., Thorburn, D. R., Trounce, I. A., Cooper, M. E., & Forbes, J. M. (2016). Mapping time-course mitochondrial adaptations in the kidney in experimental diabetes. Clinical Science, 130(9), 711–720. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20150838
Adamo, R. F., Fishbein, I., Zhang, K., Wen, J., Levy, R. J., Alferiev, I. S., & Chorny, M. (2016). Magnetically enhanced cell delivery for accelerating recovery of the endothelium in injured arteries. Journal of Controlled Release, 222, 169–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.12.025
Falendysz, E. A., Lopera, J. G., Lorenzsonn, F., Salzer, J. S., Hutson, C. L., Doty, J., Gallardo-Romero, N., Carroll, D. S., Osorio, J. E., & Rocke, T. E. (2015). Further Assessment of Monkeypox Virus Infection in Gambian Pouched Rats (Cricetomys gambianus) Using In Vivo Bioluminescent Imaging. PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 9(10), e0004130. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0004130
Rosen, D. A., Hilliard, J. K., Tiemann, K. M., Todd, E. M., Morley, S. C., & Hunstad, D. A. (2015). Klebsiella pneumoniae FimK Promotes Virulence in Murine Pneumonia. Journal of Infectious Diseases, jiv440. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiv440
Danan-Gotthold, M., Golan-Gerstl, R., Eisenberg, E., Meir, K., Karni, R., & Levanon, E. Y. (2015). Identification of recurrent regulated alternative splicing events across human solid tumors. Nucleic Acids Research, 43(10), 5130–5144. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv210
Gao, X., Yang, T., Liu, M., Peleli, M., Zollbrecht, C., Weitzberg, E., Lundberg, J. O., Persson, A. E. G., & Carlstrom, M. (2015). NADPH Oxidase in the Renal Microvasculature Is a Primary Target for Blood Pressure-Lowering Effects by Inorganic Nitrate and Nitrite. Hypertension, 65(1), 161–170. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.04222
Doldur-Balli, F., Ozel, M. N., Gulsuner, S., Tekinay, A. B., Ozcelik, T., Konu, O., & Adams, M. M. (2015). Characterization of a novel zebrafish (Danio rerio) gene, wdr81, associated with cerebellar ataxia, mental retardation and dysequilibrium syndrome (CAMRQ). BMC Neuroscience, 16(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12868-015-0229-4
Hezel, M. P., Liu, M., Schiffer, T. A., Larsen, F. J., Checa, A., Wheelock, C. E., Carlström, M., Lundberg, J. O., & Weitzberg, E. (2015). Effects of long-term dietary nitrate supplementation in mice. Redox Biology, 5, 234–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2015.05.004
Mootz, J. M., Benson, M. A., Heim, C. E., Crosby, H. A., Kavanaugh, J. S., Dunman, P. M., Kielian, T., Torres, V. J., & Horswill, A. R. (2015). Rot is a key regulator of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation: Rot regulates S . aureus biofilm formation. Molecular Microbiology, 96(2), 388–404. https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.12943
Kantharidis, P., Hagiwara, S., Brennan, E., & McClelland, A. D. (2015). Study of microRNA in diabetic nephropathy: Isolation, quantification and biological function: MicroRNA in diabetic nephropathy. Nephrology, 20(3), 132–139. https://doi.org/10.1111/nep.12374
Eriksson, A., Williams, M. J., Voisin, S., Hansson, I., Krishnan, A., Philippot, G., Yamskova, O., Herisson, F. M., Dnyansagar, R., Moschonis, G., Manios, Y., Chrousos, G. P., Olszewski, P. K., Frediksson, R., & Schiöth, H. B. (2015). Implication of coronin 7 in body weight regulation in humans, mice and flies. BMC Neuroscience, 16(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12868-015-0151-9
Zhang, Z., He, L., Hu, S., Wang, Y., Lai, Q., Yang, P., Yu, Q., Zhang, S., Xiong, F., Simsekyilmaz, S., Ning, Q., Li, J., Zhang, D., Zhang, H., Xiang, X., Zhou, Z., Sun, H., & Wang, C.-Y. (2015). AAL exacerbates pro-inflammatory response in macrophages by regulating Mincle/Syk/Card9 signaling along with the Nlrp3 inflammasome assembly. American Journal of Translational Research, 7(10), 1812–1825.
Hains, D. S., Chen, X., Saxena, V., Barr-Beare, E., Flemming, W., Easterling, R., Becknell, B., Schwartz, G. J., & Schwaderer, A. L. (2014). Carbonic anhydrase 2 deficiency leads to increased pyelonephritis susceptibility. AJP: Renal Physiology, 307(7), F869–F880. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00344.2014
van der Plas-Duivesteijn, S. J., Mohammed, Y., Dalebout, H., Meijer, A., Botermans, A., Hoogendijk, J. L., Henneman, A. A., Deelder, A. M., Spaink, H. P., & Palmblad, M. (2014). Identifying Proteins in Zebrafish Embryos Using Spectral Libraries Generated from Dissected Adult Organs and Tissues. Journal of Proteome Research, 13(3), 1537–1544. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr4010585
Wang, Z., Wei, M., Wang, M., Chen, L., Liu, H., Ren, Y., Shi, K., & Jiang, H. (2014). Inhibition of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor Reduces Diabetic Nephropathy in Type II Diabetes Mice. Inflammation, 37(6), 2020–2029. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9934-x
Huang, C.-C., Lou, B.-S., Hsu, F.-L., & Hou, C.-C. (2014). Use of urinary metabolomics to evaluate the effect of hyperuricemia on the kidney. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 74, 35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2014.08.017
Borschensky, C. M., & Reinacher, M. (2014). Mutations in the 3c and 7b genes of feline coronavirus in spontaneously affected FIP cats. Research in Veterinary Science, 97(2), 333–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rvsc.2014.07.016
Parra, S., Huang, X., Charbeneau, R. A., Wade, S. M., Kaur, K., Rorabaugh, B. R., & Neubig, R. R. (2014). Conditional disruption of interactions between Gαi2 and regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) proteins protects the heart from ischemic injury. BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology, 15(1), 29. https://doi.org/10.1186/2050-6511-15-29
Melero, M., García-Párraga, D., Corpa, J., Ortega, J., Rubio-Guerri, C., Crespo, J., Rivera-Arroyo, B., & Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J. (2014). First molecular detection and characterization of herpesvirus and poxvirus in a Pacific walrus (Odobenus rosmarus divergens). BMC Veterinary Research, 10(1), 968. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-014-0308-2
Becknell, B., Spencer, J. D., Carpenter, A. R., Chen, X., Singh, A., Ploeger, S., Kline, J., Ellsworth, P., Li, B., Proksch, E., Schwaderer, A. L., Hains, D. S., Justice, S. S., & McHugh, K. M. (2013). Expression and Antimicrobial Function of Beta-Defensin 1 in the Lower Urinary Tract. PLoS ONE, 8(10), e77714. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0077714
Cheng, X., Guo, S., Liu, Y., Chu, H., Hakimi, P., Berger, N. A., Hanson, R. W., & Kao, H.-Y. (2013). Ablation of Promyelocytic Leukemia Protein (PML) Re-patterns Energy Balance and Protects Mice from Obesity Induced by a Western Diet. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 288(41), 29746–29759. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.487595
Karauzum, H., Adhikari, R. P., Sarwar, J., Devi, V. S., Abaandou, L., Haudenschild, C., Mahmoudieh, M., Boroun, A. R., Vu, H., Nguyen, T., Warfield, K. L., Shulenin, S., & Aman, M. J. (2013). Structurally Designed Attenuated Subunit Vaccines for S. aureus LukS-PV and LukF-PV Confer Protection in a Mouse Bacteremia Model. PLoS ONE, 8(6), e65384. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0065384
Nakayama, K. H., Lee, C. C. I., Batchelder, C. A., & Tarantal, A. F. (2013). Tissue Specificity of Decellularized Rhesus Monkey Kidney and Lung Scaffolds. PLoS ONE, 8(5), e64134. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0064134
Hoang, H. D., Prasain, J. K., Dorand, D., & Miller, M. A. (2013). A Heterogeneous Mixture of F-Series Prostaglandins Promotes Sperm Guidance in the Caenorhabditis elegans Reproductive Tract. PLoS Genetics, 9(1), e1003271. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003271
Carlström, M., Brown, R. D., Yang, T., Hezel, M., Larsson, E., Scheffer, P. G., Teerlink, T., Lundberg, J. O., & Persson, A. E. G. (2013). L-arginine or tempol supplementation improves renal and cardiovascular function in rats with reduced renal mass and chronic high salt intake. Acta Physiologica, 207(4), 732–741. https://doi.org/10.1111/apha.12079
Rubio-Guerri, C., Melero, M., Esperón, F., Bellière, E., Arbelo, M., Crespo, J., Sierra, E., García-Párraga, D., & Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J. (2013). Unusual striped dolphin mass mortality episode related to cetacean morbillivirus in the Spanish Mediterranean sea. BMC Veterinary Research, 9(1), 106. https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-6148-9-106
Hanstein, R., Negoro, H., Patel, N. K., Charollais, A., Meda, P., Spray, D. C., Suadicani, S. O., & Scemes, E. (2013). Promises and pitfalls of a Pannexin1 transgenic mouse line. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 4. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2013.00061
Chaker, B., Samra, T. A., Datta, N. S., & Abou-Samra, A. B. (2013). Altered Responses to Cold Environment in Urocortin 1 and Corticotropin-Releasing Factor Deficient Mice. Physiology Journal, 2013, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/185767
Kumar, M., Roe, K., Nerurkar, P. V., Namekar, M., Orillo, B., Verma, S., & Nerurkar, V. R. (2012). Impaired Virus Clearance, Compromised Immune Response and Increased Mortality in Type 2 Diabetic Mice Infected with West Nile Virus. PLoS ONE, 7(8), e44682. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0044682
Hanke, M. L., Angle, A., & Kielian, T. (2012). MyD88-Dependent Signaling Influences Fibrosis and Alternative Macrophage Activation during Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Infection. PLoS ONE, 7(8), e42476. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0042476
Adhikari, R. P., Karauzum, H., Sarwar, J., Abaandou, L., Mahmoudieh, M., Boroun, A. R., Vu, H., Nguyen, T., Devi, V. S., Shulenin, S., Warfield, K. L., & Aman, M. J. (2012). Novel Structurally Designed Vaccine for S. aureus α-Hemolysin: Protection against Bacteremia and Pneumonia. PLoS ONE, 7(6), e38567. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0038567
Fox, K. A., Longo, M., Tamayo, E., Gamble, P., Makhlouf, M., Mateus, J. F., & Saade, G. R. (2012). Sex-specific effects of nicotine exposure on developmental programming of blood pressure and vascular reactivity in the C57Bl/6J mouse. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 207(3), 208.e1-208.e9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2012.06.021
Harcourt, B. E., Forbes, J. M., & Matthews, V. B. (2012). Obesity-induced renal impairment is exacerbated in interleukin-6-knockout mice: IL-6 KO worsens kidney injury in obesity. Nephrology, 17(3), 257–262. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1797.2011.01547.x
Carlstrom, M., Persson, A. E. G., Larsson, E., Hezel, M., Scheffer, P. G., Teerlink, T., Weitzberg, E., & Lundberg, J. O. (2011). Dietary nitrate attenuates oxidative stress, prevents cardiac and renal injuries, and reduces blood pressure in salt-induced hypertension. Cardiovascular Research, 89(3), 574–585. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvq366
Fox, K. A., Longo, M., Tamayo, E., Kechichian, T., Bytautiene, E., Hankins, G. D. V., Saade, G. R., & Costantine, M. M. (2011). Effects of pravastatin on mediators of vascular function in a mouse model of soluble Fms-like tyrosine kinase-1–induced preeclampsia. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 205(4), 366.e1-366.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2011.06.083
Thai, K. H., Thathireddy, A., & Hsieh, M. H. (2010). Transurethral Induction of Mouse Urinary Tract Infection. Journal of Visualized Experiments, 42. https://doi.org/10.3791/2070
Rayner, K. J., Suarez, Y., Davalos, A., Parathath, S., Fitzgerald, M. L., Tamehiro, N., Fisher, E. A., Moore, K. J., & Fernandez-Hernando, C. (2010). MiR-33 Contributes to the Regulation of Cholesterol Homeostasis. Science, 328(5985), 1570–1573. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1189862






