Ideal for Mouse Femur Homogenization
Do you spend lots of time and effort homogenizing Mouse Femur samples? The Bullet Blender® tissue homogenizer delivers high quality and superior yields. No other homogenizer comes close to delivering the Bullet Blender’s winning combination of top-quality performance and budget-friendly affordability. See below for a Mouse Femur homogenization protocol.
Save Time, Effort and Get Superior Results with
The Bullet Blender Homogenizer
Consistent and High Yield Results
Run up to 24 samples at the same time under microprocessor-controlled conditions, ensuring experimental reproducibility and high yield. Process samples from 10mg or less up to 3.5g.No Cross Contamination
No part of the Bullet Blender ever touches the tissue – the sample tubes are kept closed during homogenization. There are no probes to clean between samples.Samples Stay Cool
The Bullet Blenders’ innovative and elegant design provides convective cooling of the samples, so they do not heat up more than several degrees. In fact, our Gold+ models hold the sample temperature to about 4ºC.Easy and Convenient to Use
Just place beads and buffer along with your tissue sample in standard tubes, load tubes directly in the Bullet Blender, select time and speed, and press start.Risk Free Purchase
Thousands of peer-reviewed journal articles attest to the consistency and quality of the Bullet Blender homogenizer. We offer a 2 year warranty, extendable to 4 years, because our Bullet Blenders are reliable and last for many years.Mouse Femur Tissue Homogenization Protocol
Sample size |
See the Protocol |
| microcentrifuge tube model (up to 300 mg) | Small mouse femur samples |
| 5mL tube model (100mg – 1g) | Medium mouse femur samples |
What Else Can You Homogenize? Tough or Soft, No Problem!
The Bullet Blender can process a wide range of samples including organ tissue, cell culture, plant tissue, and small organisms. You can homogenize samples as tough as mouse femur or for gentle applications such as tissue dissociation or organelle isolation.

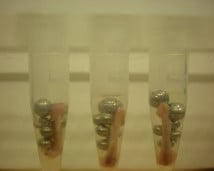

Mouse femur (on beads in upper photo) are completely homogenized into the buffer (slightly darker in lower photo).
Want more guidance? Need a quote? Contact us:

Bullet Blender Models
Select Publications using the Bullet Blender to Homogenize Mouse Femur Tissue
2474232
femur
1
apa
50
date
desc
3194
https://www.nextadvance.com/wp-content/plugins/zotpress/
%7B%22status%22%3A%22success%22%2C%22updateneeded%22%3Afalse%2C%22instance%22%3Afalse%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22request_last%22%3A0%2C%22request_next%22%3A0%2C%22used_cache%22%3Atrue%7D%2C%22data%22%3A%5B%7B%22key%22%3A%22BA9IJE67%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Heim%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015-04-15%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EHeim%2C%20C.%20E.%2C%20Vidlak%2C%20D.%2C%20Scherr%2C%20T.%20D.%2C%20Hartman%2C%20C.%20W.%2C%20Garvin%2C%20K.%20L.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Kielian%2C%20T.%20%282015%29.%20IL-12%20Promotes%20Myeloid-Derived%20Suppressor%20Cell%20Recruitment%20and%20Bacterial%20Persistence%20during%20Staphylococcus%20aureus%20Orthopedic%20Implant%20Infection.%20%3Ci%3EThe%20Journal%20of%20Immunology%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E194%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%288%29%2C%203861%26%23x2013%3B3872.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.4049%5C%2Fjimmunol.1402689%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.4049%5C%2Fjimmunol.1402689%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22IL-12%20Promotes%20Myeloid-Derived%20Suppressor%20Cell%20Recruitment%20and%20Bacterial%20Persistence%20during%20Staphylococcus%20aureus%20Orthopedic%20Implant%20Infection%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22C.%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Heim%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22D.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Vidlak%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22T.%20D.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Scherr%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22C.%20W.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hartman%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22K.%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Garvin%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22T.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kielian%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222015-04-15%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.4049%5C%2Fjimmunol.1402689%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220022-1767%2C%201550-6606%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.jimmunol.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.4049%5C%2Fjimmunol.1402689%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-12-31T20%3A16%3A05Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22DWU5M4JI%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Heim%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014-04-15%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EHeim%2C%20C.%20E.%2C%20Vidlak%2C%20D.%2C%20Scherr%2C%20T.%20D.%2C%20Kozel%2C%20J.%20A.%2C%20Holzapfel%2C%20M.%2C%20Muirhead%2C%20D.%20E.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Kielian%2C%20T.%20%282014%29.%20Myeloid-Derived%20Suppressor%20Cells%20Contribute%20to%20Staphylococcus%20aureus%20Orthopedic%20Biofilm%20Infection.%20%3Ci%3EThe%20Journal%20of%20Immunology%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E192%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%288%29%2C%203778%26%23x2013%3B3792.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.4049%5C%2Fjimmunol.1303408%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.4049%5C%2Fjimmunol.1303408%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Myeloid-Derived%20Suppressor%20Cells%20Contribute%20to%20Staphylococcus%20aureus%20Orthopedic%20Biofilm%20Infection%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22C.%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Heim%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22D.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Vidlak%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22T.%20D.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Scherr%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kozel%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Holzapfel%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22D.%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Muirhead%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22T.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kielian%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222014-04-15%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.4049%5C%2Fjimmunol.1303408%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220022-1767%2C%201550-6606%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.jimmunol.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.4049%5C%2Fjimmunol.1303408%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222016-01-12T17%3A01%3A39Z%22%7D%7D%5D%7D
Heim, C. E., Vidlak, D., Scherr, T. D., Hartman, C. W., Garvin, K. L., & Kielian, T. (2015). IL-12 Promotes Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell Recruitment and Bacterial Persistence during Staphylococcus aureus Orthopedic Implant Infection. The Journal of Immunology, 194(8), 3861–3872. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1402689
Heim, C. E., Vidlak, D., Scherr, T. D., Kozel, J. A., Holzapfel, M., Muirhead, D. E., & Kielian, T. (2014). Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Contribute to Staphylococcus aureus Orthopedic Biofilm Infection. The Journal of Immunology, 192(8), 3778–3792. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1303408






