Ideal for Muscle Tissue Homogenization
Do you spend lots of time and effort homogenizing muscle tissue samples? The Bullet Blender® tissue homogenizer delivers high quality and superior yields. No other homogenizer comes close to delivering the Bullet Blender’s winning combination of top-quality performance and budget-friendly affordability. See below for muscle tissue homogenization protocol.
Save Time, Effort and Get Superior Results with
The Bullet Blender Homogenizer
Consistent and High Yield Results
Run up to 24 samples at the same time under microprocessor-controlled conditions, ensuring experimental reproducibility and high yield. Process samples from 10mg or less up to 3.5g.No Cross Contamination
No part of the Bullet Blender ever touches the tissue – the sample tubes are kept closed during homogenization. There are no probes to clean between samples.Samples Stay Cool
The Bullet Blenders’ innovative and elegant design provides convective cooling of the samples, so they do not heat up more than several degrees. In fact, our Gold+ models hold the sample temperature to about 4ºC.Easy and Convenient to Use
Just place beads and buffer along with your tissue sample in standard tubes, load tubes directly in the Bullet Blender, select time and speed, and press start.Risk Free Purchase
Thousands of peer-reviewed journal articles attest to the consistency and quality of the Bullet Blender homogenizer. We offer a 2 year warranty, extendable to 4 years, because our Bullet Blenders are reliable and last for many years.Muscle Tissue Homogenization Protocol
Sample size |
See the Protocol |
| microcentrifuge tube model (up to 300 mg) | Small brain samples |
| 5mL tube model (100mg - 1g) | Medium brain samples |
| 50mL tube model (100mg - 3.5g) | Large brain samples |
What Else Can You Homogenize? Tough or Soft, No Problem!
The Bullet Blender can process a wide range of samples including organ tissue, cell culture, plant tissue, and small organisms. You can homogenize samples as tough as mouse femur or for gentle applications such as tissue dissociation or organelle isolation.

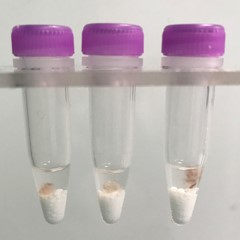
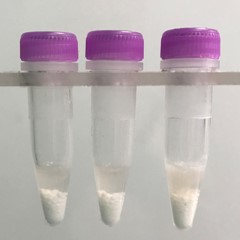
Muscle tissue pieces (on beads in upper photo) are completely homogenized into the buffer (slightly darker in lower photo).
Want more guidance? Need a quote? Contact us:

Bullet Blender Models
Select Publications using the Bullet Blender to Homogenize Muscle Tissue
2474232
muscle
1
apa
50
date
desc
3200
https://www.nextadvance.com/wp-content/plugins/zotpress/
%7B%22status%22%3A%22success%22%2C%22updateneeded%22%3Afalse%2C%22instance%22%3Afalse%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22request_last%22%3A50%2C%22request_next%22%3A50%2C%22used_cache%22%3Atrue%7D%2C%22data%22%3A%5B%7B%22key%22%3A%223FL5TVV7%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Sarasamma%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222018-12-03%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3ESarasamma%2C%20S.%2C%20Audira%2C%20G.%2C%20Juniardi%2C%20S.%2C%20Sampurna%2C%20B.%2C%20Lai%2C%20Y.-H.%2C%20Hao%2C%20E.%2C%20Chen%2C%20J.-R.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Hsiao%2C%20C.-D.%20%282018%29.%20Evaluation%20of%20the%20Effects%20of%20Carbon%2060%20Nanoparticle%20Exposure%20to%20Adult%20Zebrafish%3A%20A%20Behavioral%20and%20Biochemical%20Approach%20to%20Elucidate%20the%20Mechanism%20of%20Toxicity.%20%3Ci%3EInternational%20Journal%20of%20Molecular%20Sciences%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E19%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2812%29%2C%203853.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3390%5C%2Fijms19123853%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3390%5C%2Fijms19123853%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Evaluation%20of%20the%20Effects%20of%20Carbon%2060%20Nanoparticle%20Exposure%20to%20Adult%20Zebrafish%3A%20A%20Behavioral%20and%20Biochemical%20Approach%20to%20Elucidate%20the%20Mechanism%20of%20Toxicity%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Sreeja%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sarasamma%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Gilbert%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Audira%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Stevhen%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Juniardi%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Bonifasius%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sampurna%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Yu-Heng%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lai%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Erwei%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hao%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jung-Ren%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Chen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Chung-Der%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hsiao%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22There%20is%20a%20growing%20concern%20for%20the%20potential%20toxicity%20of%20engineered%20nanomaterials%20that%20have%20made%20their%20way%20into%20virtually%20all%20novel%20applications%20in%20the%20electronics%2C%20healthcare%2C%20cosmetics%2C%20technology%2C%20and%20engineering%20industries%2C%20and%20in%20particular%2C%20biomedical%20products.%20However%2C%20the%20potential%20toxicity%20of%20carbon%2060%20%28C60%29%20at%20the%20behavioral%20level%20has%20not%20been%20properly%20evaluated.%20In%20this%20study%2C%20we%20used%20idTracker%2C%20a%20multitracking%20algorithm%20to%20quantitatively%20assess%20behavioral%20toxicity%20induced%20by%20C60%20nanoparticles%20%28C60%20NPs%29%20in%20adult%20zebrafish.%20We%20demonstrated%20that%20locomotion%2C%20novel%20tank%20exploration%2C%20aggression%2C%20shoaling%2C%20and%20color%20preference%20activities%20of%20the%20C60%20NPs-treated%20fish%20was%20significantly%20reduced.%20In%20addition%2C%20the%20C60%20NPs-treated%20fish%20also%20displayed%20dysregulation%20of%20the%20circadian%20rhythm%20by%20showing%20lower%20locomotion%20activities%20in%20both%20day%20and%20night%20cycles.%20The%20biochemical%20results%20showed%20that%20C60%20NPs%20exposure%20at%20low%20concentration%20induced%20oxidative%20stress%20and%20DNA%20damage%2C%20reduced%20anti-oxidative%20capacity%20and%20ATP%20%28adenosine%20triphosphate%29%20levels%2C%20and%20induced%20stress-associated%20hormones%2C%20hypoxia%2C%20as%20well%20as%20inflammation%20marker%20upregulation%20in%20muscle%20and%20gill%20tissues.%20Together%2C%20this%20work%2C%20for%20the%20first%20time%2C%20provide%20direct%20evidence%20showing%20that%20the%20chronic%20exposure%20of%20C60%20NPs%20induced%20multiple%20behavioral%20abnormalities%20in%20adult%20zebrafish.%20Our%20findings%20suggest%20that%20the%20ecotoxicity%20of%20C60%20NPs%20towards%20aquatic%20vertebrates%20should%20be%20carefully%20evaluated.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222018-12-03%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.3390%5C%2Fijms19123853%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221422-0067%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.mdpi.com%5C%2F1422-0067%5C%2F19%5C%2F12%5C%2F3853%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-01-23T21%3A37%3A10Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22R5M8KTK8%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Ohana%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222016-07-15%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EOhana%2C%20D.%2C%20Dalebout%2C%20H.%2C%20Marissen%2C%20R.%20J.%2C%20Wulff%2C%20T.%2C%20Bergquist%2C%20J.%2C%20Deelder%2C%20A.%20M.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Palmblad%2C%20M.%20%282016%29.%20Identification%20of%20meat%20products%20by%20shotgun%20spectral%20matching.%20%3Ci%3EFood%20Chemistry%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E203%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%2028%26%23x2013%3B34.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.foodchem.2016.01.138%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.foodchem.2016.01.138%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Identification%20of%20meat%20products%20by%20shotgun%20spectral%20matching%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22D.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ohana%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22H.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Dalebout%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22R.%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Marissen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22T.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wulff%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Bergquist%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Deelder%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Palmblad%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22A%20new%20method%2C%20based%20on%20shotgun%20spectral%20matching%20of%20peptide%20tandem%20mass%20spectra%2C%20was%20successfully%20applied%20to%20the%20identification%20of%20different%20food%20species.%20The%20method%20was%20demonstrated%20to%20work%20on%20raw%20as%20well%20as%20processed%20samples%20from%2016%20mammalian%20and%2010%20bird%20species%20by%20counting%20spectral%20matches%20to%20spectral%20libraries%20in%20a%20reference%20database%20with%20one%20spectral%20library%20per%20species.%20A%20phylogenetic%20tree%20could%20also%20be%20constructed%20directly%20from%20the%20spectra.%20Nearly%20all%20samples%20could%20be%20correctly%20identified%20at%20the%20species%20level%2C%20and%20100%25%20at%20the%20genus%20level.%20The%20method%20does%20not%20use%20any%20genomic%20information%20and%20unlike%20targeted%20methods%2C%20no%20prior%20knowledge%20of%20genetic%20variation%20within%20a%20genus%20or%20species%20is%20necessary.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22July%2015%2C%202016%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.foodchem.2016.01.138%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220308-8146%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.sciencedirect.com%5C%2Fscience%5C%2Farticle%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS030881461630139X%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222016-06-10T17%3A54%3A59Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22TFETHPB9%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Metzger%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222016-06%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EMetzger%2C%20D.%20C.%20H.%2C%20Hemmer-Hansen%2C%20J.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Schulte%2C%20P.%20M.%20%282016%29.%20Conserved%20structure%20and%20expression%20of%20hsp70%20paralogs%20in%20teleost%20fishes.%20%3Ci%3EComparative%20Biochemistry%20and%20Physiology%20Part%20D%3A%20Genomics%20and%20Proteomics%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E18%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%2010%26%23x2013%3B20.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.cbd.2016.01.007%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.cbd.2016.01.007%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Conserved%20structure%20and%20expression%20of%20hsp70%20paralogs%20in%20teleost%20fishes%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22David%20C.%20H.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Metzger%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jakob%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hemmer-Hansen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Patricia%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Schulte%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22The%20cytosolic%2070%20KDa%20heat%20shock%20proteins%20%28Hsp70s%29%20are%20widely%20used%20as%20biomarkers%20of%20environmental%20stress%20in%20ecological%20and%20toxicological%20studies%20in%20fish.%20Here%20we%20analyze%20teleost%20genome%20sequences%20to%20show%20that%20two%20genes%20encoding%20inducible%20hsp70s%20%28hsp70-1%20and%20hsp70-2%29%20are%20likely%20present%20in%20all%20teleost%20fish.%20Phylogenetic%20and%20synteny%20analyses%20indicate%20that%20hsp70-1%20and%20hsp70-2%20are%20distinct%20paralogs%20that%20originated%20prior%20to%20the%20diversification%20of%20the%20teleosts.%20The%20promoters%20of%20both%20genes%20contain%20a%20TATA%20box%20and%20conserved%20heat%20shock%20elements%20%28HSEs%29%2C%20but%20unlike%20mammalian%20HSP70s%2C%20both%20genes%20contain%20an%20intron%20in%20the%205%5Cu2032%20UTR.%20The%20hsp70-2%20gene%20has%20undergone%20tandem%20duplication%20in%20several%20species.%20In%20addition%2C%20many%20other%20teleost%20genome%20assemblies%20have%20multiple%20copies%20of%20hsp70-2%20present%20on%20separate%2C%20small%2C%20genomic%20scaffolds.%20To%20verify%20that%20these%20represent%20poorly%20assembled%20tandem%20duplicates%2C%20we%20cloned%20the%20genomic%20region%20surrounding%20hsp70-2%20in%20Fundulus%20heteroclitus%20and%20showed%20that%20the%20hsp70-2%20gene%20copies%20that%20are%20on%20separate%20scaffolds%20in%20the%20genome%20assembly%20are%20arranged%20as%20tandem%20duplicates.%20Real-time%20quantitative%20PCR%20of%20F.%20heteroclitus%20genomic%20DNA%20indicates%20that%20four%20copies%20of%20the%20hsp70-2%20gene%20are%20likely%20present%20in%20the%20F.%20heteroclitus%20genome.%20Comparison%20of%20expression%20patterns%20in%20F.%20heteroclitus%20and%20Gasterosteus%20aculeatus%20demonstrates%20that%20hsp70-2%20has%20a%20higher%20fold%20increase%20than%20hsp70-1%20following%20heat%20shock%20in%20gill%20but%20not%20in%20muscle%20tissue%2C%20revealing%20a%20conserved%20difference%20in%20expression%20patterns%20between%20isoforms%20and%20tissues.%20These%20data%20indicate%20that%20ecological%20and%20toxicological%20studies%20using%20hsp70%20as%20a%20biomarker%20in%20teleosts%20should%20take%20this%20complexity%20into%20account.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22June%202016%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.cbd.2016.01.007%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221744-117X%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.sciencedirect.com%5C%2Fscience%5C%2Farticle%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS1744117X1630003X%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222016-06-24T17%3A01%3A46Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22IWFP5FPV%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Bouley%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222016-05-26%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EBouley%2C%20R.%2C%20Ding%2C%20D.%2C%20Peng%2C%20Z.%2C%20Bastian%2C%20M.%2C%20Lastochkin%2C%20E.%2C%20Song%2C%20W.%2C%20Suckow%2C%20M.%20A.%2C%20Schroeder%2C%20V.%20A.%2C%20Wolter%2C%20W.%20R.%2C%20Mobashery%2C%20S.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Chang%2C%20M.%20%282016%29.%20Structure%26%23x2013%3BActivity%20Relationship%20for%20the%204%283H%29-Quinazolinone%20Antibacterials.%20%3Ci%3EJournal%20of%20Medicinal%20Chemistry%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E59%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2810%29%2C%205011%26%23x2013%3B5021.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1021%5C%2Facs.jmedchem.6b00372%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1021%5C%2Facs.jmedchem.6b00372%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Structure%5Cu2013Activity%20Relationship%20for%20the%204%283H%29-Quinazolinone%20Antibacterials%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Renee%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Bouley%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Derong%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ding%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Zhihong%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Peng%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Maria%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Bastian%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Elena%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lastochkin%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Wei%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Song%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mark%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Suckow%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Valerie%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Schroeder%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22William%20R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wolter%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Shahriar%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Mobashery%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mayland%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Chang%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22We%20recently%20reported%20on%20the%20discovery%20of%20a%20novel%20antibacterial%20%282%29%20with%20a%204%283H%29-quinazolinone%20core.%20This%20discovery%20was%20made%20by%20in%20silico%20screening%20of%201.2%20million%20compounds%20for%20binding%20to%20a%20penicillin-binding%20protein%20and%20the%20subsequent%20demonstration%20of%20antibacterial%20activity%20against%20Staphylococcus%20aureus.%20The%20first%20structure%5Cu2013activity%20relationship%20for%20this%20antibacterial%20scaffold%20is%20explored%20in%20this%20report%20with%20evaluation%20of%2077%20variants%20of%20the%20structural%20class.%20Eleven%20promising%20compounds%20were%20further%20evaluated%20for%20in%20vitro%20toxicity%2C%20pharmacokinetics%2C%20and%20efficacy%20in%20a%20mouse%20peritonitis%20model%20of%20infection%2C%20which%20led%20to%20the%20discovery%20of%20compound%2027.%20This%20new%20quinazolinone%20has%20potent%20activity%20against%20methicillin-resistant%20%28MRSA%29%20strains%2C%20low%20clearance%2C%20oral%20bioavailability%20and%20shows%20efficacy%20in%20a%20mouse%20neutropenic%20thigh%20infection%20model.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22May%2026%2C%202016%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1021%5C%2Facs.jmedchem.6b00372%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220022-2623%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdx.doi.org%5C%2F10.1021%5C%2Facs.jmedchem.6b00372%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222016-06-10T19%3A23%3A57Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22978CTNF8%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Luethy%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222016%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3ELuethy%2C%20L.%20N.%2C%20Erickson%2C%20A.%20K.%2C%20Jesudhasan%2C%20P.%20R.%2C%20Ikizler%2C%20M.%2C%20Dermody%2C%20T.%20S.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Pfeiffer%2C%20J.%20K.%20%282016%29.%20Comparison%20of%20three%20neurotropic%20viruses%20reveals%20differences%20in%20viral%20dissemination%20to%20the%20central%20nervous%20system.%20%3Ci%3EVirology%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E487%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%201%26%23x2013%3B10.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.virol.2015.09.019%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.virol.2015.09.019%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Comparison%20of%20three%20neurotropic%20viruses%20reveals%20differences%20in%20viral%20dissemination%20to%20the%20central%20nervous%20system%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Lauren%20N.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Luethy%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Andrea%20K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Erickson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Palmy%20R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Jesudhasan%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mine%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ikizler%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Terence%20S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Dermody%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Julie%20K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Pfeiffer%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2201%5C%2F2016%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.virol.2015.09.019%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2200426822%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0042682215004109%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222016-06-24T16%3A47%3A52Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22QQUGU3XB%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Albury-Warren%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015-10-20%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EAlbury-Warren%2C%20T.%20M.%2C%20Pandey%2C%20V.%2C%20Spinel%2C%20L.%20P.%2C%20Masternak%2C%20M.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Altomare%2C%20D.%20A.%20%282015%29.%20Prediabetes%20linked%20to%20excess%20glucagon%20in%20transgenic%20mice%20with%20pancreatic%20active%20AKT1.%20%3Ci%3EJournal%20of%20Endocrinology%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20JOE-15-0288.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1530%5C%2FJOE-15-0288%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1530%5C%2FJOE-15-0288%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Prediabetes%20linked%20to%20excess%20glucagon%20in%20transgenic%20mice%20with%20pancreatic%20active%20AKT1%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Toya%20Marquita%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Albury-Warren%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Veethika%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Pandey%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Lina%20P%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Spinel%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Michal%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Masternak%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Deborah%20A%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Altomare%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222015-10-20%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1530%5C%2FJOE-15-0288%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220022-0795%2C%201479-6805%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fjoe.endocrinology-journals.org%5C%2Flookup%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1530%5C%2FJOE-15-0288%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-10-30T19%3A59%3A18Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22IDSWFQMG%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Larsen%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015-10-09%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3ELarsen%2C%20F.%20J.%2C%20Schiffer%2C%20T.%20A.%2C%20Ortenblad%2C%20N.%2C%20Zinner%2C%20C.%2C%20Morales-Alamo%2C%20D.%2C%20Willis%2C%20S.%20J.%2C%20Calbet%2C%20J.%20A.%2C%20Holmberg%2C%20H.-C.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Boushel%2C%20R.%20%282015%29.%20High-intensity%20sprint%20training%20inhibits%20mitochondrial%20respiration%20through%20aconitase%20inactivation.%20%3Ci%3EThe%20FASEB%20Journal%3C%5C%2Fi%3E.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1096%5C%2Ffj.15-276857%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1096%5C%2Ffj.15-276857%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22High-intensity%20sprint%20training%20inhibits%20mitochondrial%20respiration%20through%20aconitase%20inactivation%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22F.%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Larsen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22T.%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Schiffer%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22N.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ortenblad%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22C.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Zinner%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22D.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Morales-Alamo%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22S.%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Willis%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Calbet%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22H.-C.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Holmberg%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Boushel%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222015-10-09%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1096%5C%2Ffj.15-276857%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220892-6638%2C%201530-6860%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.fasebj.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1096%5C%2Ffj.15-276857%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-12-30T16%3A49%3A43Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22M4F7J42E%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22An%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015-08-10%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EAn%2C%20C.%2C%20Bhetwal%2C%20B.%20P.%2C%20Sanders%2C%20K.%20M.%2C%20Somlyo%2C%20A.%20V.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Perrino%2C%20B.%20A.%20%282015%29.%20Role%20of%20Telokin%20in%20Regulating%20Murine%20Gastric%20Fundus%20Smooth%20Muscle%20Tension.%20%3Ci%3EPLOS%20ONE%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E10%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%288%29%2C%20e0134876.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0134876%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0134876%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Role%20of%20Telokin%20in%20Regulating%20Murine%20Gastric%20Fundus%20Smooth%20Muscle%20Tension%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Changlong%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22An%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Bhupal%20P.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Bhetwal%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kenton%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sanders%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Avril%20V.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Somlyo%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Brian%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Perrino%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Agustin%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Guerrero-Hernandez%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222015-8-10%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0134876%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221932-6203%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdx.plos.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0134876%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-10-30T20%3A36%3A47Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22N4AXZ4KQ%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Hurley-Sanders%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015-06-20%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EHurley-Sanders%2C%20J.%20L.%2C%20Levine%2C%20J.%20F.%2C%20Nelson%2C%20S.%20A.%20C.%2C%20Law%2C%20J.%20M.%2C%20Showers%2C%20W.%20J.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Stoskopf%2C%20M.%20K.%20%282015%29.%20Key%20metabolites%20in%20tissue%20extracts%20of%20Elliptio%20complanata%20identified%20using%201H%20nuclear%20magnetic%20resonance%20spectroscopy.%20%3Ci%3EConservation%20Physiology%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E3%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%281%29%2C%20cov023%26%23x2013%3Bcov023.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fconphys%5C%2Fcov023%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fconphys%5C%2Fcov023%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Key%20metabolites%20in%20tissue%20extracts%20of%20Elliptio%20complanata%20identified%20using%201H%20nuclear%20magnetic%20resonance%20spectroscopy%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hurley-Sanders%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%20F.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Levine%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22S.%20A.%20C.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Nelson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Law%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22W.%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Showers%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%20K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Stoskopf%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222015-06-20%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1093%5C%2Fconphys%5C%2Fcov023%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%222051-1434%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fconphys.oxfordjournals.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fconphys%5C%2Fcov023%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-08-05T13%3A23%3A24Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22MC25AFV5%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Moore%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015-05-25%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EMoore%2C%20C.%20D.%2C%20Fahlman%2C%20A.%2C%20Crocker%2C%20D.%20E.%2C%20Robbins%2C%20K.%20A.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Trumble%2C%20S.%20J.%20%282015%29.%20The%20degradation%20of%20proteins%20in%20pinniped%20skeletal%20muscle%3A%20viability%20of%20post-mortem%20tissue%20in%20physiological%20research.%20%3Ci%3EConservation%20Physiology%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E3%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%281%29%2C%20cov019%26%23x2013%3Bcov019.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fconphys%5C%2Fcov019%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fconphys%5C%2Fcov019%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22The%20degradation%20of%20proteins%20in%20pinniped%20skeletal%20muscle%3A%20viability%20of%20post-mortem%20tissue%20in%20physiological%20research%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22C.%20D.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Moore%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fahlman%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22D.%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Crocker%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22K.%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Robbins%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22S.%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Trumble%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222015-05-25%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1093%5C%2Fconphys%5C%2Fcov019%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%222051-1434%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fconphys.oxfordjournals.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fconphys%5C%2Fcov019%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-12-30T19%3A51%3A46Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22N999XXEI%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Vechetti-Junior%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015-05-19%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EVechetti-Junior%2C%20I.%20J.%2C%20Bertaglia%2C%20R.%20S.%2C%20Fernandez%2C%20G.%20J.%2C%20de%20Paula%2C%20T.%20G.%2C%20de%20Souza%2C%20R.%20W.%20A.%2C%20Moraes%2C%20L.%20N.%2C%20Mareco%2C%20E.%20A.%2C%20de%20Freitas%2C%20C.%20E.%20A.%2C%20Aguiar%2C%20A.%20F.%2C%20Carvalho%2C%20R.%20F.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Dal-Pai-Silva%2C%20M.%20%282015%29.%20Aerobic%20Exercise%20Recovers%20Disuse-induced%20Atrophy%20Through%20the%20Stimulus%20of%20the%20LRP130%5C%2FPGC-1%20Complex%20in%20Aged%20Rats.%20%3Ci%3EThe%20Journals%20of%20Gerontology%20Series%20A%3A%20Biological%20Sciences%20and%20Medical%20Sciences%3C%5C%2Fi%3E.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fgerona%5C%2Fglv064%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fgerona%5C%2Fglv064%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Aerobic%20Exercise%20Recovers%20Disuse-induced%20Atrophy%20Through%20the%20Stimulus%20of%20the%20LRP130%5C%2FPGC-1%20Complex%20in%20Aged%20Rats%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22I.%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Vechetti-Junior%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22R.%20S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Bertaglia%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22G.%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fernandez%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22T.%20G.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22de%20Paula%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22R.%20W.%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22de%20Souza%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22L.%20N.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Moraes%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22E.%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Mareco%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22C.%20E.%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22de%20Freitas%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%20F.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Aguiar%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22R.%20F.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Carvalho%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Dal-Pai-Silva%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222015-05-19%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1093%5C%2Fgerona%5C%2Fglv064%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221079-5006%2C%201758-535X%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fbiomedgerontology.oxfordjournals.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fgerona%5C%2Fglv064%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-10-30T20%3A55%3A34Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%2243E5RM2N%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Lynch%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015-04-20%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3ELynch%2C%20C.%20J.%2C%20Xu%2C%20Y.%2C%20Hajnal%2C%20A.%2C%20Salzberg%2C%20A.%20C.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Kawasawa%2C%20Y.%20I.%20%282015%29.%20RNA%20Sequencing%20Reveals%20a%20Slow%20to%20Fast%20Muscle%20Fiber%20Type%20Transition%20after%20Olanzapine%20Infusion%20in%20Rats.%20%3Ci%3EPLOS%20ONE%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E10%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%284%29%2C%20e0123966.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0123966%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0123966%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22RNA%20Sequencing%20Reveals%20a%20Slow%20to%20Fast%20Muscle%20Fiber%20Type%20Transition%20after%20Olanzapine%20Infusion%20in%20Rats%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Christopher%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lynch%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Yuping%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Xu%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Andras%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hajnal%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Anna%20C.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Salzberg%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Yuka%20Imamura%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kawasawa%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Guillermo%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22L%5Cu00f3pez%20Lluch%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222015-4-20%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0123966%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221932-6203%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdx.plos.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0123966%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-08-06T16%3A20%3A12Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22S6E4TGNM%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Zheng%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015-02-15%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EZheng%2C%20X.%2C%20Reho%2C%20J.%20J.%2C%20Wirth%2C%20B.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Fisher%2C%20S.%20A.%20%282015%29.%20TRA2%26%23x3B2%3B%20controls%20Mypt1%20exon%2024%20splicing%20in%20the%20developmental%20maturation%20of%20mouse%20mesenteric%20artery%20smooth%20muscle.%20%3Ci%3EAmerican%20Journal%20of%20Physiology%20-%20Cell%20Physiology%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E308%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%284%29%2C%20C289%26%23x2013%3BC296.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1152%5C%2Fajpcell.00304.2014%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1152%5C%2Fajpcell.00304.2014%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22TRA2%5Cu03b2%20controls%20Mypt1%20exon%2024%20splicing%20in%20the%20developmental%20maturation%20of%20mouse%20mesenteric%20artery%20smooth%20muscle%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Xiaoxu%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Zheng%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22John%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Reho%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Brunhilde%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wirth%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Steven%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fisher%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222015-02-15%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1152%5C%2Fajpcell.00304.2014%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220363-6143%2C%201522-1563%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fajpcell.physiology.org%5C%2Flookup%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1152%5C%2Fajpcell.00304.2014%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-08-03T16%3A08%3A12Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22NUGCIXQF%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Doldur-Balli%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EDoldur-Balli%2C%20F.%2C%20Ozel%2C%20M.%20N.%2C%20Gulsuner%2C%20S.%2C%20Tekinay%2C%20A.%20B.%2C%20Ozcelik%2C%20T.%2C%20Konu%2C%20O.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Adams%2C%20M.%20M.%20%282015%29.%20Characterization%20of%20a%20novel%20zebrafish%20%28Danio%20rerio%29%20gene%2C%20wdr81%2C%20associated%20with%20cerebellar%20ataxia%2C%20mental%20retardation%20and%20dysequilibrium%20syndrome%20%28CAMRQ%29.%20%3Ci%3EBMC%20Neuroscience%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E16%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%281%29.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1186%5C%2Fs12868-015-0229-4%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1186%5C%2Fs12868-015-0229-4%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Characterization%20of%20a%20novel%20zebrafish%20%28Danio%20rerio%29%20gene%2C%20wdr81%2C%20associated%20with%20cerebellar%20ataxia%2C%20mental%20retardation%20and%20dysequilibrium%20syndrome%20%28CAMRQ%29%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Fusun%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Doldur-Balli%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mehmet%20Neset%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ozel%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Suleyman%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Gulsuner%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ayse%20B.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Tekinay%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Tayfun%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ozcelik%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ozlen%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Konu%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Michelle%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Adams%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2212%5C%2F2015%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1186%5C%2Fs12868-015-0229-4%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221471-2202%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.biomedcentral.com%5C%2F1471-2202%5C%2F16%5C%2F96%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-12-30T18%3A54%3A48Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22QPR7SA52%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Frank%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EFrank%2C%20P.%2C%20Andersson%2C%20E.%2C%20Pont%26%23xE9%3Bn%2C%20M.%2C%20Ekblom%2C%20B.%2C%20Ekblom%2C%20M.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Sahlin%2C%20K.%20%282015%29.%20Strength%20training%20improves%20muscle%20aerobic%20capacity%20and%20glucose%20tolerance%20in%20elderly%3A%20Strength%20training%20in%20elderly.%20%3Ci%3EScandinavian%20Journal%20of%20Medicine%20%26amp%3B%20Science%20in%20Sports%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20n%5C%2Fa-n%5C%2Fa.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fsms.12537%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fsms.12537%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Strength%20training%20improves%20muscle%20aerobic%20capacity%20and%20glucose%20tolerance%20in%20elderly%3A%20Strength%20training%20in%20elderly%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22P.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Frank%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Andersson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Pont%5Cu00e9n%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22B.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ekblom%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ekblom%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sahlin%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2209%5C%2F2015%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1111%5C%2Fsms.12537%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2209057188%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.wiley.com%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fsms.12537%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-12-30T16%3A09%3A58Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22WHXVE3A9%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Psilander%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EPsilander%2C%20N.%2C%20Frank%2C%20P.%2C%20Flockhart%2C%20M.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Sahlin%2C%20K.%20%282015%29.%20Adding%20strength%20to%20endurance%20training%20does%20not%20enhance%20aerobic%20capacity%20in%20cyclists%3A%20Concurrent%20training%20mitochondrial%20biogenesis.%20%3Ci%3EScandinavian%20Journal%20of%20Medicine%20%26amp%3B%20Science%20in%20Sports%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E25%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%284%29%2C%20e353%26%23x2013%3Be359.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fsms.12338%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fsms.12338%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Adding%20strength%20to%20endurance%20training%20does%20not%20enhance%20aerobic%20capacity%20in%20cyclists%3A%20Concurrent%20training%20mitochondrial%20biogenesis%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22N.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Psilander%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22P.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Frank%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Flockhart%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sahlin%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2208%5C%2F2015%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1111%5C%2Fsms.12338%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2209057188%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.wiley.com%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fsms.12338%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-29T16%3A08%3A09Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%222IEVS26G%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Neishabouri%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3ENeishabouri%2C%20S.%20H.%2C%20Hutson%2C%20S.%20M.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Davoodi%2C%20J.%20%282015%29.%20Chronic%20activation%20of%20mTOR%20complex%201%20by%20branched%20chain%20amino%20acids%20and%20organ%20hypertrophy.%20%3Ci%3EAmino%20Acids%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E47%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%286%29%2C%201167%26%23x2013%3B1182.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1007%5C%2Fs00726-015-1944-y%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1007%5C%2Fs00726-015-1944-y%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Chronic%20activation%20of%20mTOR%20complex%201%20by%20branched%20chain%20amino%20acids%20and%20organ%20hypertrophy%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22S.%20Hallaj%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Neishabouri%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22S.%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hutson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Davoodi%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%226%5C%2F2015%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1007%5C%2Fs00726-015-1944-y%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220939-4451%2C%201438-2199%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flink.springer.com%5C%2F10.1007%5C%2Fs00726-015-1944-y%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-31T16%3A24%3A29Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%227DJ6IRZ9%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Alves%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EAlves%2C%20R.%20D.%20A.%20M.%2C%20Dane%2C%20A.%20D.%2C%20Harms%2C%20A.%2C%20Strassburg%2C%20K.%2C%20Seifar%2C%20R.%20M.%2C%20Verdijk%2C%20L.%20B.%2C%20Kersten%2C%20S.%2C%20Berger%2C%20R.%2C%20Hankemeier%2C%20T.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Vreeken%2C%20R.%20J.%20%282015%29.%20Global%20profiling%20of%20the%20muscle%20metabolome%3A%20method%20optimization%2C%20validation%20and%20application%20to%20determine%20exercise-induced%20metabolic%20effects.%20%3Ci%3EMetabolomics%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E11%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%282%29%2C%20271%26%23x2013%3B285.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1007%5C%2Fs11306-014-0701-7%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1007%5C%2Fs11306-014-0701-7%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Global%20profiling%20of%20the%20muscle%20metabolome%3A%20method%20optimization%2C%20validation%20and%20application%20to%20determine%20exercise-induced%20metabolic%20effects%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Rodrigo%20D.%20A.%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Alves%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Adrie%20D.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Dane%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Amy%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Harms%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Katrin%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Strassburg%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Reza%20Maleki%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Seifar%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Lex%20B.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Verdijk%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Sander%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kersten%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ruud%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Berger%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Thomas%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hankemeier%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Rob%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Vreeken%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%224%5C%2F2015%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1007%5C%2Fs11306-014-0701-7%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221573-3882%2C%201573-3890%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flink.springer.com%5C%2F10.1007%5C%2Fs11306-014-0701-7%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-29T16%3A18%3A40Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22W8C3GMRX%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Mootz%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EMootz%2C%20J.%20M.%2C%20Benson%2C%20M.%20A.%2C%20Heim%2C%20C.%20E.%2C%20Crosby%2C%20H.%20A.%2C%20Kavanaugh%2C%20J.%20S.%2C%20Dunman%2C%20P.%20M.%2C%20Kielian%2C%20T.%2C%20Torres%2C%20V.%20J.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Horswill%2C%20A.%20R.%20%282015%29.%20Rot%20is%20a%20key%20regulator%20of%20%3Ci%3EStaphylococcus%20aureus%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%20biofilm%20formation%3A%20Rot%20regulates%20%3Ci%3ES%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%20%3Ci%3E.%20aureus%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%20biofilm%20formation.%20%3Ci%3EMolecular%20Microbiology%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E96%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%282%29%2C%20388%26%23x2013%3B404.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fmmi.12943%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fmmi.12943%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Rot%20is%20a%20key%20regulator%20of%20%3Ci%3EStaphylococcus%20aureus%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%20biofilm%20formation%3A%20Rot%20regulates%20%3Ci%3ES%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%20%3Ci%3E.%20aureus%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%20biofilm%20formation%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Joe%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Mootz%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Meredith%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Benson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Cortney%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Heim%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Heidi%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Crosby%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jeffrey%20S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kavanaugh%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Paul%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Dunman%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Tammy%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kielian%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Victor%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Torres%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Alexander%20R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Horswill%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2204%5C%2F2015%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1111%5C%2Fmmi.12943%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220950382X%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.wiley.com%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fmmi.12943%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222016-01-11T20%3A28%3A45Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22V29MHE7G%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Tomechko%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3ETomechko%2C%20S.%20E.%2C%20Liu%2C%20G.%2C%20Tao%2C%20M.%2C%20Schlatzer%2C%20D.%2C%20Powell%2C%20C.%20T.%2C%20Gupta%2C%20S.%2C%20Chance%2C%20M.%20R.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Daneshgari%2C%20F.%20%282015%29.%20Tissue%20Specific%20Dysregulated%20Protein%20Subnetworks%20in%20Type%202%20Diabetic%20Bladder%20Urothelium%20and%20Detrusor%20Muscle.%20%3Ci%3EMolecular%20%26amp%3B%20Cellular%20Proteomics%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E14%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%283%29%2C%20635%26%23x2013%3B645.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1074%5C%2Fmcp.M114.041863%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1074%5C%2Fmcp.M114.041863%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Tissue%20Specific%20Dysregulated%20Protein%20Subnetworks%20in%20Type%202%20Diabetic%20Bladder%20Urothelium%20and%20Detrusor%20Muscle%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Sara%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Tomechko%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Guiming%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Liu%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mingfang%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Tao%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Daniela%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Schlatzer%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22C.%20Thomas%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Powell%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Sanjay%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Gupta%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mark%20R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Chance%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Firouz%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Daneshgari%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2203%5C%2F2015%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1074%5C%2Fmcp.M114.041863%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221535-9476%2C%201535-9484%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.mcponline.org%5C%2Flookup%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1074%5C%2Fmcp.M114.041863%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-10-16T19%3A47%3A12Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22PVP7RHGH%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Do%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EDo%2C%20A.%2C%20Menon%2C%20V.%2C%20Zhi%2C%20X.%2C%20Gesing%2C%20A.%2C%20Wiesenborn%2C%20D.%2C%20Spong%2C%20A.%2C%20Sun%2C%20L.%2C%20Bartke%2C%20A.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Masternak%2C%20M.%20M.%20%282015%29.%20Thyroxine%20modifies%20the%20effects%20of%20growth%20hormone%20in%20Ames%20dwarf%20mice.%20%3Ci%3EAging%20%28Albany%2C%20NY%29%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E7%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%284%29%2C%20241%26%23x2013%3B255.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-ItemURL%27%20href%3D%27http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov%5C%2Fpmc%5C%2Farticles%5C%2FPMC4429089%5C%2F%27%3Ehttp%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov%5C%2Fpmc%5C%2Farticles%5C%2FPMC4429089%5C%2F%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Thyroxine%20modifies%20the%20effects%20of%20growth%20hormone%20in%20Ames%20dwarf%20mice%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Andrew%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Do%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Vinal%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Menon%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Xu%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Zhi%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Adam%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Gesing%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Denise%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wiesenborn%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Adam%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Spong%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Liou%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sun%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Andrzej%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Bartke%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Michal%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Masternak%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%22%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%22%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov%5C%2Fpmc%5C%2Farticles%5C%2FPMC4429089%5C%2F%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-12-30T19%3A44%3A52Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22J63E8CF5%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Pi%5Cu00f3rkowska%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EPi%26%23xF3%3Brkowska%2C%20K.%2C%20Nowak%2C%20J.%2C%20Po%26%23x142%3Btowicz%2C%20K.%2C%20Ropka-Molik%2C%20K.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Szmato%26%23x142%3Ba%2C%20T.%20%282015%29.%20Effect%20of%20newly%20found%20polymorphisms%20in%20the%20promoter%20region%20of%20the%20CAPN1%20gene%20on%20transcript%20abundance%20in%20broiler%20chicken%20breast%20muscle.%20%3Ci%3EAnimal%20Science%20Papers%20and%20Reports%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E33%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%283%29%2C%20287%26%23x2013%3B298.%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Effect%20of%20newly%20found%20polymorphisms%20in%20the%20promoter%20region%20of%20the%20CAPN1%20gene%20on%20transcript%20abundance%20in%20broiler%20chicken%20breast%20muscle%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Katarzyna%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Pi%5Cu00f3rkowska%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Joanna%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Nowak%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Katarzyna%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Po%5Cu0142towicz%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Katarzyna%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ropka-Molik%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Tomasz%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Szmato%5Cu0142a%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%22%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%22%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-12-30T18%3A46%3A42Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22795N92G2%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Psilander%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014-12-19%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EPsilander%2C%20N.%20%282014%29.%20%3Ci%3EThe%20effect%20of%20different%20exercise%20regimens%20on%20mitochondrial%20biogenesis%20and%20performance%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%20%5BKarolinska%20Instituet%5D.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-ItemURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fopenarchive.ki.se%5C%2Fxmlui%5C%2Fbitstream%5C%2Fhandle%5C%2F10616%5C%2F42310%5C%2FThesis_Niklas_Psilander.pdf%3Fsequence%3D3%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fopenarchive.ki.se%5C%2Fxmlui%5C%2Fbitstream%5C%2Fhandle%5C%2F10616%5C%2F42310%5C%2FThesis_Niklas_Psilander.pdf%3Fsequence%3D3%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22thesis%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22The%20effect%20of%20different%20exercise%20regimens%20on%20mitochondrial%20biogenesis%20and%20performance%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Niklas%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Psilander%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22thesisType%22%3A%22%22%2C%22university%22%3A%22Karolinska%20Instituet%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2212-19-2014%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fopenarchive.ki.se%5C%2Fxmlui%5C%2Fbitstream%5C%2Fhandle%5C%2F10616%5C%2F42310%5C%2FThesis_Niklas_Psilander.pdf%3Fsequence%3D3%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222016-01-13T18%3A48%3A25Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22XC2SPJ3M%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Drake%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014-11-01%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EDrake%2C%20J.%20C.%2C%20Bruns%2C%20D.%20R.%2C%20Peelor%2C%20F.%20F.%2C%20Biela%2C%20L.%20M.%2C%20Miller%2C%20R.%20A.%2C%20Hamilton%2C%20K.%20L.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Miller%2C%20B.%20F.%20%282014%29.%20Long-lived%20crowded-litter%20mice%20have%20an%20age-dependent%20increase%20in%20protein%20synthesis%20to%20DNA%20synthesis%20ratio%20and%20mTORC1%20substrate%20phosphorylation.%20%3Ci%3EAJP%3A%20Endocrinology%20and%20Metabolism%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E307%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%289%29%2C%20E813%26%23x2013%3BE821.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1152%5C%2Fajpendo.00256.2014%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1152%5C%2Fajpendo.00256.2014%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Long-lived%20crowded-litter%20mice%20have%20an%20age-dependent%20increase%20in%20protein%20synthesis%20to%20DNA%20synthesis%20ratio%20and%20mTORC1%20substrate%20phosphorylation%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%20C.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Drake%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22D.%20R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Bruns%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22F.%20F.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Peelor%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22L.%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Biela%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22R.%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Miller%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22K.%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hamilton%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22B.%20F.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Miller%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222014-11-01%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1152%5C%2Fajpendo.00256.2014%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220193-1849%2C%201522-1555%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fajpendo.physiology.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1152%5C%2Fajpendo.00256.2014%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-12-01T16%3A23%3A55Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22BHR3AU2D%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Moore%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014-06-10%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EMoore%2C%20C.%20D.%2C%20Crocker%2C%20D.%20E.%2C%20Fahlman%2C%20A.%2C%20Moore%2C%20M.%20J.%2C%20Willoughby%2C%20D.%20S.%2C%20Robbins%2C%20K.%20A.%2C%20Kanatous%2C%20S.%20B.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Trumble%2C%20S.%20J.%20%282014%29.%20Ontogenetic%20changes%20in%20skeletal%20muscle%20fiber%20type%2C%20fiber%20diameter%20and%20myoglobin%20concentration%20in%20the%20Northern%20elephant%20seal%20%28Mirounga%20angustirostris%29.%20%3Ci%3EFrontiers%20in%20Physiology%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E5%3C%5C%2Fi%3E.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3389%5C%2Ffphys.2014.00217%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.3389%5C%2Ffphys.2014.00217%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Ontogenetic%20changes%20in%20skeletal%20muscle%20fiber%20type%2C%20fiber%20diameter%20and%20myoglobin%20concentration%20in%20the%20Northern%20elephant%20seal%20%28Mirounga%20angustirostris%29%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Colby%20D.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Moore%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Daniel%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Crocker%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Andreas%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fahlman%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Michael%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Moore%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Darryn%20S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Willoughby%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kathleen%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Robbins%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Shane%20B.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kanatous%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Stephen%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Trumble%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222014-06-10%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.3389%5C%2Ffphys.2014.00217%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221664-042X%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fjournal.frontiersin.org%5C%2Farticle%5C%2F10.3389%5C%2Ffphys.2014.00217%5C%2Fabstract%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-10-30T20%3A03%3A10Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%2268VMAP2U%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22King%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014-05-16%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EKing%2C%20I.%20N.%2C%20Yartseva%2C%20V.%2C%20Salas%2C%20D.%2C%20Kumar%2C%20A.%2C%20Heidersbach%2C%20A.%2C%20Ando%2C%20D.%20M.%2C%20Stallings%2C%20N.%20R.%2C%20Elliott%2C%20J.%20L.%2C%20Srivastava%2C%20D.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Ivey%2C%20K.%20N.%20%282014%29.%20The%20RNA-binding%20Protein%20TDP-43%20Selectively%20Disrupts%20MicroRNA-1%5C%2F206%20Incorporation%20into%20the%20RNA-induced%20Silencing%20Complex.%20%3Ci%3EJournal%20of%20Biological%20Chemistry%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E289%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2820%29%2C%2014263%26%23x2013%3B14271.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1074%5C%2Fjbc.M114.561902%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1074%5C%2Fjbc.M114.561902%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22The%20RNA-binding%20Protein%20TDP-43%20Selectively%20Disrupts%20MicroRNA-1%5C%2F206%20Incorporation%20into%20the%20RNA-induced%20Silencing%20Complex%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22I.%20N.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22King%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22V.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Yartseva%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22D.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Salas%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kumar%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Heidersbach%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22D.%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ando%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22N.%20R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Stallings%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Elliott%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22D.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Srivastava%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22K.%20N.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ivey%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222014-05-16%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1074%5C%2Fjbc.M114.561902%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220021-9258%2C%201083-351X%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.jbc.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1074%5C%2Fjbc.M114.561902%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-10-30T20%3A21%3A12Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%226X5P59RJ%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22van%20der%20Plas-Duivesteijn%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014-03-07%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3Evan%20der%20Plas-Duivesteijn%2C%20S.%20J.%2C%20Mohammed%2C%20Y.%2C%20Dalebout%2C%20H.%2C%20Meijer%2C%20A.%2C%20Botermans%2C%20A.%2C%20Hoogendijk%2C%20J.%20L.%2C%20Henneman%2C%20A.%20A.%2C%20Deelder%2C%20A.%20M.%2C%20Spaink%2C%20H.%20P.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Palmblad%2C%20M.%20%282014%29.%20Identifying%20Proteins%20in%20Zebrafish%20Embryos%20Using%20Spectral%20Libraries%20Generated%20from%20Dissected%20Adult%20Organs%20and%20Tissues.%20%3Ci%3EJournal%20of%20Proteome%20Research%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E13%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%283%29%2C%201537%26%23x2013%3B1544.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1021%5C%2Fpr4010585%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1021%5C%2Fpr4010585%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Identifying%20Proteins%20in%20Zebrafish%20Embryos%20Using%20Spectral%20Libraries%20Generated%20from%20Dissected%20Adult%20Organs%20and%20Tissues%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Suzanne%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22van%20der%20Plas-Duivesteijn%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Yassene%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Mohammed%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Hans%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Dalebout%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Annemarie%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Meijer%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Anouk%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Botermans%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jordy%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hoogendijk%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Alex%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Henneman%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Andr%5Cu00e9%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Deelder%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Herman%20P.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Spaink%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Magnus%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Palmblad%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222014-03-07%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1021%5C%2Fpr4010585%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221535-3893%2C%201535-3907%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fpubs.acs.org%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2Fabs%5C%2F10.1021%5C%2Fpr4010585%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-08-10T16%3A33%3A28Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22T4TSXDH2%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Verhaart%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014-02-18%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EVerhaart%2C%20I.%20E.%20C.%2C%20van%20Vliet-van%20den%20Dool%2C%20L.%2C%20Sipkens%2C%20J.%20A.%2C%20de%20Kimpe%2C%20S.%20J.%2C%20Kolfschoten%2C%20I.%20G.%20M.%2C%20van%20Deutekom%2C%20J.%20C.%20T.%2C%20Liefaard%2C%20L.%2C%20Ridings%2C%20J.%20E.%2C%20Hood%2C%20S.%20R.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Aartsma-Rus%2C%20A.%20%282014%29.%20The%20Dynamics%20of%20Compound%2C%20Transcript%2C%20and%20Protein%20Effects%20After%20Treatment%20With%202OMePS%20Antisense%20Oligonucleotides%20in%20mdx%20Mice.%20%3Ci%3EMolecular%20Therapy%26%23x2014%3BNucleic%20Acids%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E3%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%282%29%2C%20e148.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1038%5C%2Fmtna.2014.1%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1038%5C%2Fmtna.2014.1%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22The%20Dynamics%20of%20Compound%2C%20Transcript%2C%20and%20Protein%20Effects%20After%20Treatment%20With%202OMePS%20Antisense%20Oligonucleotides%20in%20mdx%20Mice%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ingrid%20E%20C%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Verhaart%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Laura%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22van%20Vliet-van%20den%20Dool%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jessica%20A%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sipkens%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Sjef%20J%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22de%20Kimpe%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ingrid%20G%20M%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kolfschoten%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Judith%20C%20T%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22van%20Deutekom%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Lia%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Liefaard%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jim%20E%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ridings%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Steve%20R%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hood%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Annemieke%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Aartsma-Rus%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222014-2-18%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1038%5C%2Fmtna.2014.1%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%222162-2531%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.nature.com%5C%2Fdoifinder%5C%2F10.1038%5C%2Fmtna.2014.1%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-17T15%3A37%3A13Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22X6BIEHBX%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Mathewson%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EMathewson%2C%20M.%20A.%2C%20Chambers%2C%20H.%20G.%2C%20Girard%2C%20P.%20J.%2C%20Tenenhaus%2C%20M.%2C%20Schwartz%2C%20A.%20K.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Lieber%2C%20R.%20L.%20%282014%29.%20Stiff%20muscle%20fibers%20in%20calf%20muscles%20of%20patients%20with%20cerebral%20palsy%20lead%20to%20high%20passive%20muscle%20stiffness%3A%20CP%20CALF%20MUSCLE%20FIBER%20STIFFNESS.%20%3Ci%3EJournal%20of%20Orthopaedic%20Research%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E32%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2812%29%2C%201667%26%23x2013%3B1674.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1002%5C%2Fjor.22719%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1002%5C%2Fjor.22719%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Stiff%20muscle%20fibers%20in%20calf%20muscles%20of%20patients%20with%20cerebral%20palsy%20lead%20to%20high%20passive%20muscle%20stiffness%3A%20CP%20CALF%20MUSCLE%20FIBER%20STIFFNESS%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Margie%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Mathewson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Henry%20G.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Chambers%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Paul%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Girard%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mayer%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Tenenhaus%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Alexandra%20K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Schwartz%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Richard%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lieber%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2212%5C%2F2014%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1002%5C%2Fjor.22719%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2207360266%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.wiley.com%5C%2F10.1002%5C%2Fjor.22719%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-10-30T19%3A58%3A10Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%229ZIQ7WRT%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Lashgari%20and%20Lee%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3ELashgari%2C%20M.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Lee%2C%20H.%20K.%20%282014%29.%20Determination%20of%20perfluorinated%20carboxylic%20acids%20in%20fish%20fillet%20by%20micro-solid%20phase%20extraction%2C%20followed%20by%20liquid%20chromatography%26%23x2013%3Btriple%20quadrupole%20mass%20spectrometry.%20%3Ci%3EJournal%20of%20Chromatography%20A%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E1369%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%2026%26%23x2013%3B32.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.chroma.2014.09.082%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.chroma.2014.09.082%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Determination%20of%20perfluorinated%20carboxylic%20acids%20in%20fish%20fillet%20by%20micro-solid%20phase%20extraction%2C%20followed%20by%20liquid%20chromatography%5Cu2013triple%20quadrupole%20mass%20spectrometry%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Maryam%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lashgari%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Hian%20Kee%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lee%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2211%5C%2F2014%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.chroma.2014.09.082%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2200219673%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0021967314015520%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-08-10T16%3A13%3A58Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22PQDU2QVQ%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Mukund%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EMukund%2C%20K.%2C%20Mathewson%2C%20M.%2C%20Minamoto%2C%20V.%2C%20Ward%2C%20S.%20R.%2C%20Subramaniam%2C%20S.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Lieber%2C%20R.%20L.%20%282014%29.%20Systems%20analysis%20of%20transcriptional%20data%20provides%20insights%20into%20muscle%26%23x2019%3Bs%20biological%20response%20to%20botulinum%20toxin%3A%20Transcriptional%20Profiling%20after%20BoNT-A.%20%3Ci%3EMuscle%20%26amp%3B%20Nerve%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E50%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%285%29%2C%20744%26%23x2013%3B758.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1002%5C%2Fmus.24211%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1002%5C%2Fmus.24211%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Systems%20analysis%20of%20transcriptional%20data%20provides%20insights%20into%20muscle%27s%20biological%20response%20to%20botulinum%20toxin%3A%20Transcriptional%20Profiling%20after%20BoNT-A%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kavitha%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Mukund%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Margie%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Mathewson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Viviane%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Minamoto%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Samuel%20R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ward%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Shankar%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Subramaniam%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Richard%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lieber%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2211%5C%2F2014%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1002%5C%2Fmus.24211%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220148639X%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.wiley.com%5C%2F10.1002%5C%2Fmus.24211%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-08-10T16%3A48%3A02Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22GSSNRUMU%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Menon%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EMenon%2C%20V.%2C%20Zhi%2C%20X.%2C%20Hossain%2C%20T.%2C%20Bartke%2C%20A.%2C%20Spong%2C%20A.%2C%20Gesing%2C%20A.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Masternak%2C%20M.%20M.%20%282014%29.%20The%20contribution%20of%20visceral%20fat%20to%20improved%20insulin%20signaling%20in%20Ames%20dwarf%20mice.%20%3Ci%3EAging%20Cell%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E13%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%283%29%2C%20497%26%23x2013%3B506.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Facel.12201%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Facel.12201%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22The%20contribution%20of%20visceral%20fat%20to%20improved%20insulin%20signaling%20in%20Ames%20dwarf%20mice%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Vinal%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Menon%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Xu%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Zhi%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Tanvir%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hossain%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Andrzej%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Bartke%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Adam%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Spong%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Adam%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Gesing%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Michal%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Masternak%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2206%5C%2F2014%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1111%5C%2Facel.12201%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2214749718%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.wiley.com%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Facel.12201%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-21T13%3A59%3A57Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22CG63U65K%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Melero%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EMelero%2C%20M.%2C%20Garc%26%23xED%3Ba-P%26%23xE1%3Brraga%2C%20D.%2C%20Corpa%2C%20J.%2C%20Ortega%2C%20J.%2C%20Rubio-Guerri%2C%20C.%2C%20Crespo%2C%20J.%2C%20Rivera-Arroyo%2C%20B.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20S%26%23xE1%3Bnchez-Vizca%26%23xED%3Bno%2C%20J.%20%282014%29.%20First%20molecular%20detection%20and%20characterization%20of%20herpesvirus%20and%20poxvirus%20in%20a%20Pacific%20walrus%20%28Odobenus%20rosmarus%20divergens%29.%20%3Ci%3EBMC%20Veterinary%20Research%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E10%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%281%29%2C%20968.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1186%5C%2Fs12917-014-0308-2%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1186%5C%2Fs12917-014-0308-2%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22First%20molecular%20detection%20and%20characterization%20of%20herpesvirus%20and%20poxvirus%20in%20a%20Pacific%20walrus%20%28Odobenus%20rosmarus%20divergens%29%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mar%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Melero%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Daniel%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Garc%5Cu00eda-P%5Cu00e1rraga%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Juan%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Corpa%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Joaqu%5Cu00edn%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ortega%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Consuelo%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Rubio-Guerri%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jos%5Cu00e9%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Crespo%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Bel%5Cu00e9n%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Rivera-Arroyo%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jos%5Cu00e9%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22S%5Cu00e1nchez-Vizca%5Cu00edno%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222014%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1186%5C%2Fs12917-014-0308-2%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221746-6148%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.biomedcentral.com%5C%2F1746-6148%5C%2F10%5C%2F968%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222016-01-12T17%3A25%3A07Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22UXME5RD5%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Schuh%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3ESchuh%2C%20R.%20A.%2C%20Jackson%2C%20K.%20C.%2C%20Schlappal%2C%20A.%20E.%2C%20Spangenburg%2C%20E.%20E.%2C%20Ward%2C%20C.%20W.%2C%20Park%2C%20J.%20H.%2C%20Dugger%2C%20N.%2C%20Shi%2C%20G.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Fishman%2C%20P.%20S.%20%282014%29.%20Mitochondrial%20oxygen%20consumption%20deficits%20in%20skeletal%20muscle%20isolated%20from%20an%20Alzheimer%26%23x2019%3Bs%20disease-relevant%20murine%20model.%20%3Ci%3EBMC%20Neuroscience%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E15%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%281%29%2C%2024.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1186%5C%2F1471-2202-15-24%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1186%5C%2F1471-2202-15-24%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Mitochondrial%20oxygen%20consumption%20deficits%20in%20skeletal%20muscle%20isolated%20from%20an%20Alzheimer%5Cu2019s%20disease-relevant%20murine%20model%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Rosemary%20A%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Schuh%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Kathryn%20C%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Jackson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Anna%20E%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Schlappal%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Espen%20E%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Spangenburg%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Christopher%20W%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ward%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ji%20H%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Park%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Natalie%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Dugger%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Guo%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Shi%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Paul%20S%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fishman%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222014%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1186%5C%2F1471-2202-15-24%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221471-2202%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.biomedcentral.com%5C%2F1471-2202%5C%2F15%5C%2F24%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-17T15%3A35%3A43Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%228WGEEFKN%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Drake%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013-12-01%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EDrake%2C%20J.%20C.%2C%20Peelor%2C%20F.%20F.%2C%20Biela%2C%20L.%20M.%2C%20Watkins%2C%20M.%20K.%2C%20Miller%2C%20R.%20A.%2C%20Hamilton%2C%20K.%20L.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Miller%2C%20B.%20F.%20%282013%29.%20Assessment%20of%20Mitochondrial%20Biogenesis%20and%20mTORC1%20Signaling%20During%20Chronic%20Rapamycin%20Feeding%20in%20Male%20and%20Female%20Mice.%20%3Ci%3EThe%20Journals%20of%20Gerontology%20Series%20A%3A%20Biological%20Sciences%20and%20Medical%20Sciences%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E68%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2812%29%2C%201493%26%23x2013%3B1501.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fgerona%5C%2Fglt047%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fgerona%5C%2Fglt047%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Assessment%20of%20Mitochondrial%20Biogenesis%20and%20mTORC1%20Signaling%20During%20Chronic%20Rapamycin%20Feeding%20in%20Male%20and%20Female%20Mice%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%20C.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Drake%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22F.%20F.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Peelor%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22L.%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Biela%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%20K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Watkins%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22R.%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Miller%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22K.%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hamilton%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22B.%20F.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Miller%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013-12-01%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1093%5C%2Fgerona%5C%2Fglt047%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221079-5006%2C%201758-535X%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fbiomedgerontology.oxfordjournals.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fgerona%5C%2Fglt047%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-20T16%3A20%3A05Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22N9BNIMJV%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Erickson%20and%20Pfeiffer%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013-11-15%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EErickson%2C%20A.%20K.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Pfeiffer%2C%20J.%20K.%20%282013%29.%20Dynamic%20Viral%20Dissemination%20in%20Mice%20Infected%20with%20Yellow%20Fever%20Virus%20Strain%2017D.%20%3Ci%3EJournal%20of%20Virology%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E87%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2822%29%2C%2012392%26%23x2013%3B12397.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1128%5C%2FJVI.02149-13%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1128%5C%2FJVI.02149-13%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Dynamic%20Viral%20Dissemination%20in%20Mice%20Infected%20with%20Yellow%20Fever%20Virus%20Strain%2017D%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%20K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Erickson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%20K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Pfeiffer%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013-11-15%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1128%5C%2FJVI.02149-13%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220022-538X%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fjvi.asm.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1128%5C%2FJVI.02149-13%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-20T16%3A31%3A52Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%225ZPHANX4%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Cheng%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013-10-11%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3ECheng%2C%20X.%2C%20Guo%2C%20S.%2C%20Liu%2C%20Y.%2C%20Chu%2C%20H.%2C%20Hakimi%2C%20P.%2C%20Berger%2C%20N.%20A.%2C%20Hanson%2C%20R.%20W.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Kao%2C%20H.-Y.%20%282013%29.%20Ablation%20of%20Promyelocytic%20Leukemia%20Protein%20%28PML%29%20Re-patterns%20Energy%20Balance%20and%20Protects%20Mice%20from%20Obesity%20Induced%20by%20a%20Western%20Diet.%20%3Ci%3EJournal%20of%20Biological%20Chemistry%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E288%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2841%29%2C%2029746%26%23x2013%3B29759.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1074%5C%2Fjbc.M113.487595%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1074%5C%2Fjbc.M113.487595%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Ablation%20of%20Promyelocytic%20Leukemia%20Protein%20%28PML%29%20Re-patterns%20Energy%20Balance%20and%20Protects%20Mice%20from%20Obesity%20Induced%20by%20a%20Western%20Diet%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22X.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Cheng%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Guo%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Y.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Liu%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22H.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Chu%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22P.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hakimi%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22N.%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Berger%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22R.%20W.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hanson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22H.-Y.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kao%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013-10-11%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1074%5C%2Fjbc.M113.487595%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220021-9258%2C%201083-351X%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.jbc.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1074%5C%2Fjbc.M113.487595%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-20T16%3A09%3A49Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22KTFVUP8J%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Miller%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013-05-01%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EMiller%2C%20B.%20F.%2C%20Robinson%2C%20M.%20M.%2C%20Reuland%2C%20D.%20J.%2C%20Drake%2C%20J.%20C.%2C%20Peelor%2C%20F.%20F.%2C%20Bruss%2C%20M.%20D.%2C%20Hellerstein%2C%20M.%20K.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Hamilton%2C%20K.%20L.%20%282013%29.%20Calorie%20Restriction%20Does%20Not%20Increase%20Short-term%20or%20Long-term%20Protein%20Synthesis.%20%3Ci%3EThe%20Journals%20of%20Gerontology%20Series%20A%3A%20Biological%20Sciences%20and%20Medical%20Sciences%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E68%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%285%29%2C%20530%26%23x2013%3B538.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fgerona%5C%2Fgls219%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fgerona%5C%2Fgls219%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Calorie%20Restriction%20Does%20Not%20Increase%20Short-term%20or%20Long-term%20Protein%20Synthesis%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22B.%20F.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Miller%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Robinson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22D.%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Reuland%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%20C.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Drake%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22F.%20F.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Peelor%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%20D.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Bruss%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%20K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hellerstein%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22K.%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hamilton%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013-05-01%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1093%5C%2Fgerona%5C%2Fgls219%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221079-5006%2C%201758-535X%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fbiomedgerontology.oxfordjournals.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fgerona%5C%2Fgls219%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-21T14%3A15%3A17Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%228C5R2NZW%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Mcgowan%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013-04-03%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EMcgowan%2C%20I.%2C%20Hoesley%2C%20C.%2C%20Cranston%2C%20R.%20D.%2C%20Andrew%2C%20P.%2C%20Janocko%2C%20L.%2C%20Dai%2C%20J.%20Y.%2C%20Carballo-Dieguez%2C%20A.%2C%20Ayudhya%2C%20R.%20K.%20N.%2C%20Piper%2C%20J.%2C%20Hladik%2C%20F.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Mayer%2C%20K.%20%282013%29.%20A%20Phase%201%20Randomized%2C%20Double%20Blind%2C%20Placebo%20Controlled%20Rectal%20Safety%20and%20Acceptability%20Study%20of%20Tenofovir%201%25%20Gel%20%28MTN-007%29.%20%3Ci%3EPLoS%20ONE%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E8%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%284%29%2C%20e60147.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0060147%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0060147%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22A%20Phase%201%20Randomized%2C%20Double%20Blind%2C%20Placebo%20Controlled%20Rectal%20Safety%20and%20Acceptability%20Study%20of%20Tenofovir%201%25%20Gel%20%28MTN-007%29%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ian%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Mcgowan%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Craig%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hoesley%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ross%20D.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Cranston%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Philip%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Andrew%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Laura%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Janocko%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22James%20Y.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Dai%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Alex%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Carballo-Dieguez%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ratiya%20Kunjara%20Na%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ayudhya%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jeanna%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Piper%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Florian%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hladik%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ken%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Mayer%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Willem%20Daniel%20Francois%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Venter%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013-4-3%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0060147%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221932-6203%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdx.plos.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fjournal.pone.0060147%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-13T14%3A17%3A24Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%227KT8C7QM%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Moghadaszadeh%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013-04-01%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EMoghadaszadeh%2C%20B.%2C%20Rider%2C%20B.%20E.%2C%20Lawlor%2C%20M.%20W.%2C%20Childers%2C%20M.%20K.%2C%20Grange%2C%20R.%20W.%2C%20Gupta%2C%20K.%2C%20Boukedes%2C%20S.%20S.%2C%20Owen%2C%20C.%20A.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Beggs%2C%20A.%20H.%20%282013%29.%20Selenoprotein%20N%20deficiency%20in%20mice%20is%20associated%20with%20abnormal%20lung%20development.%20%3Ci%3EThe%20FASEB%20Journal%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E27%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%284%29%2C%201585%26%23x2013%3B1599.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1096%5C%2Ffj.12-212688%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1096%5C%2Ffj.12-212688%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Selenoprotein%20N%20deficiency%20in%20mice%20is%20associated%20with%20abnormal%20lung%20development%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22B.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Moghadaszadeh%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22B.%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Rider%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%20W.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lawlor%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%20K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Childers%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22R.%20W.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Grange%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Gupta%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22S.%20S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Boukedes%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22C.%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Owen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%20H.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Beggs%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013-04-01%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1096%5C%2Ffj.12-212688%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220892-6638%2C%201530-6860%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.fasebj.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1096%5C%2Ffj.12-212688%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-22T13%3A44%3A22Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22T98EXXJJ%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Gao%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013-03-15%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EGao%2C%20N.%2C%20Huang%2C%20J.%2C%20He%2C%20W.%2C%20Zhu%2C%20M.%2C%20Kamm%2C%20K.%20E.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Stull%2C%20J.%20T.%20%282013%29.%20Signaling%20through%20Myosin%20Light%20Chain%20Kinase%20in%20Smooth%20Muscles.%20%3Ci%3EJournal%20of%20Biological%20Chemistry%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E288%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2811%29%2C%207596%26%23x2013%3B7605.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1074%5C%2Fjbc.M112.427112%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1074%5C%2Fjbc.M112.427112%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Signaling%20through%20Myosin%20Light%20Chain%20Kinase%20in%20Smooth%20Muscles%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22N.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Gao%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Huang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22W.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22He%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Zhu%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22K.%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kamm%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%20T.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Stull%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013-03-15%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1074%5C%2Fjbc.M112.427112%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220021-9258%2C%201083-351X%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.jbc.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1074%5C%2Fjbc.M112.427112%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-13T16%3A38%3A44Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22IBPZH6RB%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Hanke%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013-03-01%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EHanke%2C%20M.%20L.%2C%20Heim%2C%20C.%20E.%2C%20Angle%2C%20A.%2C%20Sanderson%2C%20S.%20D.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Kielian%2C%20T.%20%282013%29.%20Targeting%20Macrophage%20Activation%20for%20the%20Prevention%20and%20Treatment%20of%20Staphylococcus%20aureus%20Biofilm%20Infections.%20%3Ci%3EThe%20Journal%20of%20Immunology%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E190%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%285%29%2C%202159%26%23x2013%3B2168.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.4049%5C%2Fjimmunol.1202348%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.4049%5C%2Fjimmunol.1202348%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Targeting%20Macrophage%20Activation%20for%20the%20Prevention%20and%20Treatment%20of%20Staphylococcus%20aureus%20Biofilm%20Infections%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%20L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hanke%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22C.%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Heim%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Angle%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22S.%20D.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sanderson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22T.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Kielian%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013-03-01%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.4049%5C%2Fjimmunol.1202348%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220022-1767%2C%201550-6606%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.jimmunol.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.4049%5C%2Fjimmunol.1202348%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-17T15%3A22%3A24Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22FQKBUQMG%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Frank%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013-02-15%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EFrank%2C%20P.%2C%20Katz%2C%20A.%2C%20Andersson%2C%20E.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Sahlin%2C%20K.%20%282013%29.%20Acute%20exercise%20reverses%20starvation-mediated%20insulin%20resistance%20in%20humans.%20%3Ci%3EAJP%3A%20Endocrinology%20and%20Metabolism%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E304%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%284%29%2C%20E436%26%23x2013%3BE443.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1152%5C%2Fajpendo.00416.2012%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1152%5C%2Fajpendo.00416.2012%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Acute%20exercise%20reverses%20starvation-mediated%20insulin%20resistance%20in%20humans%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22P.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Frank%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Katz%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Andersson%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sahlin%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013-02-15%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1152%5C%2Fajpendo.00416.2012%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220193-1849%2C%201522-1555%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fajpendo.physiology.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1152%5C%2Fajpendo.00416.2012%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-10T15%3A07%3A39Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%227RA2TABI%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Percival%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013-01-01%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EPercival%2C%20J.%20M.%2C%20Siegel%2C%20M.%20P.%2C%20Knowels%2C%20G.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Marcinek%2C%20D.%20J.%20%282013%29.%20Defects%20in%20mitochondrial%20localization%20and%20ATP%20synthesis%20in%20the%20mdx%20mouse%20model%20of%20Duchenne%20muscular%20dystrophy%20are%20not%20alleviated%20by%20PDE5%20inhibition.%20%3Ci%3EHuman%20Molecular%20Genetics%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E22%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%281%29%2C%20153%26%23x2013%3B167.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fhmg%5C%2Fdds415%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fhmg%5C%2Fdds415%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Defects%20in%20mitochondrial%20localization%20and%20ATP%20synthesis%20in%20the%20mdx%20mouse%20model%20of%20Duchenne%20muscular%20dystrophy%20are%20not%20alleviated%20by%20PDE5%20inhibition%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Percival%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%20P.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Siegel%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22G.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Knowels%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22D.%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Marcinek%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013-01-01%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1093%5C%2Fhmg%5C%2Fdds415%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220964-6906%2C%201460-2083%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.hmg.oxfordjournals.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1093%5C%2Fhmg%5C%2Fdds415%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-17T15%3A30%3A46Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22K27F692F%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Riisager%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3ERiisager%2C%20M.%2C%20Duno%2C%20M.%2C%20Hansen%2C%20F.%20J.%2C%20Krag%2C%20T.%20O.%2C%20Vissing%2C%20C.%20R.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Vissing%2C%20J.%20%282013%29.%20A%20new%20mutation%20of%20the%20fukutin%20gene%20causing%20late-onset%20limb%20girdle%20muscular%20dystrophy.%20%3Ci%3ENeuromuscular%20Disorders%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E23%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%287%29%2C%20562%26%23x2013%3B567.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.nmd.2013.04.006%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.nmd.2013.04.006%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22A%20new%20mutation%20of%20the%20fukutin%20gene%20causing%20late-onset%20limb%20girdle%20muscular%20dystrophy%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Riisager%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Duno%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22F.%20Juul%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hansen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22T.O.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Krag%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22C.R.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Vissing%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Vissing%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%227%5C%2F2013%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.nmd.2013.04.006%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2209608966%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0960896613001399%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-10T15%3A16%3A18Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22UZJDXN4X%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Brault%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EBrault%2C%20J.%20J.%2C%20Pizzimenti%2C%20N.%20M.%2C%20Dentel%2C%20J.%20N.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Wiseman%2C%20R.%20W.%20%282013%29.%20Selective%20inhibition%20of%20ATPase%20activity%20during%20contraction%20alters%20the%20activation%20of%20p38%20MAP%20kinase%20isoforms%20in%20skeletal%20muscle.%20%3Ci%3EJournal%20of%20Cellular%20Biochemistry%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E114%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%286%29%2C%201445%26%23x2013%3B1455.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1002%5C%2Fjcb.24486%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1002%5C%2Fjcb.24486%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Selective%20inhibition%20of%20ATPase%20activity%20during%20contraction%20alters%20the%20activation%20of%20p38%20MAP%20kinase%20isoforms%20in%20skeletal%20muscle%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jeffrey%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Brault%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Natalie%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Pizzimenti%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22John%20N.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Dentel%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Robert%20W.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wiseman%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2206%5C%2F2013%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1002%5C%2Fjcb.24486%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2207302312%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.wiley.com%5C%2F10.1002%5C%2Fjcb.24486%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-17T15%3A01%3A18Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%222I3555HZ%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Veltrop%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EVeltrop%2C%20M.%2C%20van%20der%20Kaa%2C%20J.%2C%20Claassens%2C%20J.%2C%20van%20Vliet%2C%20L.%2C%20Verbeek%2C%20S.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Aartsma-Rus%2C%20A.%20%282013%29.%20Generation%20of%20Embryonic%20Stem%20Cells%20and%20Mice%20for%20Duchenne%20Research.%20%3Ci%3EPLoS%20Currents%3C%5C%2Fi%3E.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fcurrents.md.cbf1d33001de80923ce674302cad7925%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1371%5C%2Fcurrents.md.cbf1d33001de80923ce674302cad7925%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Generation%20of%20Embryonic%20Stem%20Cells%20and%20Mice%20for%20Duchenne%20Research%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Marcel%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Veltrop%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jos%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22van%20der%20Kaa%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jill%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Claassens%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Laura%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22van%20Vliet%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Sjef%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Verbeek%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Annemieke%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Aartsma-Rus%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1371%5C%2Fcurrents.md.cbf1d33001de80923ce674302cad7925%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%222157-3999%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fcurrents.plos.org%5C%2Fmd%5C%2F%3Fp%3D3649%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-22T14%3A31%3A22Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22QHHD6XSX%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Liu%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3ELiu%2C%20B.-H.%2C%20Lin%2C%20Y.-Y.%2C%20Wang%2C%20Y.-C.%2C%20Huang%2C%20C.-W.%2C%20Chen%2C%20C.-C.%2C%20Wu%2C%20S.-C.%2C%20Mersmann%2C%20H.%20J.%2C%20Cheng%2C%20W.%20T.%20K.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Ding%2C%20S.-T.%20%282013%29.%20Porcine%20Adiponectin%20Receptor%201%20Transgene%20Resists%20High-fat%5C%2FSucrose%20Diet-Induced%20Weight%20Gain%2C%20Hepatosteatosis%20and%20Insulin%20Resistance%20in%20Mice.%20%3Ci%3EExperimental%20Animals%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E62%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%284%29%2C%20347%26%23x2013%3B360.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1538%5C%2Fexpanim.62.347%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1538%5C%2Fexpanim.62.347%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Porcine%20Adiponectin%20Receptor%201%20Transgene%20Resists%20High-fat%5C%2FSucrose%20Diet-Induced%20Weight%20Gain%2C%20Hepatosteatosis%20and%20Insulin%20Resistance%20in%20Mice%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Bing-Hsien%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Liu%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Yuan-Yu%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lin%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ya-Chin%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Chao-Wei%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Huang%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Chih-Chien%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Chen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Shinn-Chih%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wu%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Harry%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Mersmann%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Winston%20T.K.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Cheng%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Shih-Torng%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ding%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1538%5C%2Fexpanim.62.347%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221341-1357%2C%201881-7122%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fjlc.jst.go.jp%5C%2FDN%5C%2FJST.JSTAGE%5C%2Fexpanim%5C%2F62.347%3Flang%3Den%26from%3DCrossRef%26type%3Dabstract%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-20T17%3A52%3A10Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22F9ACZKNR%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Chaker%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EChaker%2C%20B.%2C%20Samra%2C%20T.%20A.%2C%20Datta%2C%20N.%20S.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Abou-Samra%2C%20A.%20B.%20%282013%29.%20Altered%20Responses%20to%20Cold%20Environment%20in%20Urocortin%201%20and%20Corticotropin-Releasing%20Factor%20Deficient%20Mice.%20%3Ci%3EPhysiology%20Journal%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E2013%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%201%26%23x2013%3B7.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1155%5C%2F2013%5C%2F185767%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1155%5C%2F2013%5C%2F185767%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Altered%20Responses%20to%20Cold%20Environment%20in%20Urocortin%201%20and%20Corticotropin-Releasing%20Factor%20Deficient%20Mice%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Bayan%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Chaker%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Tareq%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Samra%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Nabanita%20S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Datta%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Abdul%20B.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Abou-Samra%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222013%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1155%5C%2F2013%5C%2F185767%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%222314-4300%2C%202314-4319%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.hindawi.com%5C%2Fjournals%5C%2Fphysiology%5C%2F2013%5C%2F185767%5C%2F%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-20T16%3A06%3A38Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%228KZUQ376%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A2474232%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Battaglia%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222012-12-15%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A0%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%3EBattaglia%2C%20G.%20M.%2C%20Zheng%2C%20D.%2C%20Hickner%2C%20R.%20C.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Houmard%2C%20J.%20A.%20%282012%29.%20Effect%20of%20exercise%20training%20on%20metabolic%20flexibility%20in%20response%20to%20a%20high-fat%20diet%20in%20obese%20individuals.%20%3Ci%3EAJP%3A%20Endocrinology%20and%20Metabolism%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2C%20%3Ci%3E303%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%2812%29%2C%20E1440%26%23x2013%3BE1445.%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-DOIURL%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1152%5C%2Fajpendo.00355.2012%27%3Ehttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1152%5C%2Fajpendo.00355.2012%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Effect%20of%20exercise%20training%20on%20metabolic%20flexibility%20in%20response%20to%20a%20high-fat%20diet%20in%20obese%20individuals%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22G.%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Battaglia%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22D.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Zheng%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22R.%20C.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hickner%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Houmard%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222012-12-15%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1152%5C%2Fajpendo.00355.2012%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220193-1849%2C%201522-1555%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fajpendo.physiology.org%5C%2Fcgi%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1152%5C%2Fajpendo.00355.2012%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22M2MNG549%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222015-07-10T14%3A55%3A59Z%22%7D%7D%5D%7D
Sarasamma, S., Audira, G., Juniardi, S., Sampurna, B., Lai, Y.-H., Hao, E., Chen, J.-R., & Hsiao, C.-D. (2018). Evaluation of the Effects of Carbon 60 Nanoparticle Exposure to Adult Zebrafish: A Behavioral and Biochemical Approach to Elucidate the Mechanism of Toxicity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(12), 3853. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123853
Ohana, D., Dalebout, H., Marissen, R. J., Wulff, T., Bergquist, J., Deelder, A. M., & Palmblad, M. (2016). Identification of meat products by shotgun spectral matching. Food Chemistry, 203, 28–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.01.138
Metzger, D. C. H., Hemmer-Hansen, J., & Schulte, P. M. (2016). Conserved structure and expression of hsp70 paralogs in teleost fishes. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part D: Genomics and Proteomics, 18, 10–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbd.2016.01.007
Bouley, R., Ding, D., Peng, Z., Bastian, M., Lastochkin, E., Song, W., Suckow, M. A., Schroeder, V. A., Wolter, W. R., Mobashery, S., & Chang, M. (2016). Structure–Activity Relationship for the 4(3H)-Quinazolinone Antibacterials. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 59(10), 5011–5021. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00372
Luethy, L. N., Erickson, A. K., Jesudhasan, P. R., Ikizler, M., Dermody, T. S., & Pfeiffer, J. K. (2016). Comparison of three neurotropic viruses reveals differences in viral dissemination to the central nervous system. Virology, 487, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2015.09.019
Albury-Warren, T. M., Pandey, V., Spinel, L. P., Masternak, M., & Altomare, D. A. (2015). Prediabetes linked to excess glucagon in transgenic mice with pancreatic active AKT1. Journal of Endocrinology, JOE-15-0288. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-15-0288
Larsen, F. J., Schiffer, T. A., Ortenblad, N., Zinner, C., Morales-Alamo, D., Willis, S. J., Calbet, J. A., Holmberg, H.-C., & Boushel, R. (2015). High-intensity sprint training inhibits mitochondrial respiration through aconitase inactivation. The FASEB Journal. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.15-276857
An, C., Bhetwal, B. P., Sanders, K. M., Somlyo, A. V., & Perrino, B. A. (2015). Role of Telokin in Regulating Murine Gastric Fundus Smooth Muscle Tension. PLOS ONE, 10(8), e0134876. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0134876
Hurley-Sanders, J. L., Levine, J. F., Nelson, S. A. C., Law, J. M., Showers, W. J., & Stoskopf, M. K. (2015). Key metabolites in tissue extracts of Elliptio complanata identified using 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Conservation Physiology, 3(1), cov023–cov023. https://doi.org/10.1093/conphys/cov023
Moore, C. D., Fahlman, A., Crocker, D. E., Robbins, K. A., & Trumble, S. J. (2015). The degradation of proteins in pinniped skeletal muscle: viability of post-mortem tissue in physiological research. Conservation Physiology, 3(1), cov019–cov019. https://doi.org/10.1093/conphys/cov019
Vechetti-Junior, I. J., Bertaglia, R. S., Fernandez, G. J., de Paula, T. G., de Souza, R. W. A., Moraes, L. N., Mareco, E. A., de Freitas, C. E. A., Aguiar, A. F., Carvalho, R. F., & Dal-Pai-Silva, M. (2015). Aerobic Exercise Recovers Disuse-induced Atrophy Through the Stimulus of the LRP130/PGC-1 Complex in Aged Rats. The Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glv064
Lynch, C. J., Xu, Y., Hajnal, A., Salzberg, A. C., & Kawasawa, Y. I. (2015). RNA Sequencing Reveals a Slow to Fast Muscle Fiber Type Transition after Olanzapine Infusion in Rats. PLOS ONE, 10(4), e0123966. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0123966
Zheng, X., Reho, J. J., Wirth, B., & Fisher, S. A. (2015). TRA2β controls Mypt1 exon 24 splicing in the developmental maturation of mouse mesenteric artery smooth muscle. American Journal of Physiology - Cell Physiology, 308(4), C289–C296. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00304.2014
Doldur-Balli, F., Ozel, M. N., Gulsuner, S., Tekinay, A. B., Ozcelik, T., Konu, O., & Adams, M. M. (2015). Characterization of a novel zebrafish (Danio rerio) gene, wdr81, associated with cerebellar ataxia, mental retardation and dysequilibrium syndrome (CAMRQ). BMC Neuroscience, 16(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12868-015-0229-4
Frank, P., Andersson, E., Pontén, M., Ekblom, B., Ekblom, M., & Sahlin, K. (2015). Strength training improves muscle aerobic capacity and glucose tolerance in elderly: Strength training in elderly. Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports, n/a-n/a. https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.12537
Psilander, N., Frank, P., Flockhart, M., & Sahlin, K. (2015). Adding strength to endurance training does not enhance aerobic capacity in cyclists: Concurrent training mitochondrial biogenesis. Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports, 25(4), e353–e359. https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.12338
Neishabouri, S. H., Hutson, S. M., & Davoodi, J. (2015). Chronic activation of mTOR complex 1 by branched chain amino acids and organ hypertrophy. Amino Acids, 47(6), 1167–1182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-015-1944-y
Alves, R. D. A. M., Dane, A. D., Harms, A., Strassburg, K., Seifar, R. M., Verdijk, L. B., Kersten, S., Berger, R., Hankemeier, T., & Vreeken, R. J. (2015). Global profiling of the muscle metabolome: method optimization, validation and application to determine exercise-induced metabolic effects. Metabolomics, 11(2), 271–285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-014-0701-7
Mootz, J. M., Benson, M. A., Heim, C. E., Crosby, H. A., Kavanaugh, J. S., Dunman, P. M., Kielian, T., Torres, V. J., & Horswill, A. R. (2015). Rot is a key regulator of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation: Rot regulates S . aureus biofilm formation. Molecular Microbiology, 96(2), 388–404. https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.12943
Tomechko, S. E., Liu, G., Tao, M., Schlatzer, D., Powell, C. T., Gupta, S., Chance, M. R., & Daneshgari, F. (2015). Tissue Specific Dysregulated Protein Subnetworks in Type 2 Diabetic Bladder Urothelium and Detrusor Muscle. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 14(3), 635–645. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M114.041863
Do, A., Menon, V., Zhi, X., Gesing, A., Wiesenborn, D., Spong, A., Sun, L., Bartke, A., & Masternak, M. M. (2015). Thyroxine modifies the effects of growth hormone in Ames dwarf mice. Aging (Albany, NY), 7(4), 241–255. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4429089/
Piórkowska, K., Nowak, J., Połtowicz, K., Ropka-Molik, K., & Szmatoła, T. (2015). Effect of newly found polymorphisms in the promoter region of the CAPN1 gene on transcript abundance in broiler chicken breast muscle. Animal Science Papers and Reports, 33(3), 287–298.
Psilander, N. (2014). The effect of different exercise regimens on mitochondrial biogenesis and performance [Karolinska Instituet]. https://openarchive.ki.se/xmlui/bitstream/handle/10616/42310/Thesis_Niklas_Psilander.pdf?sequence=3
Drake, J. C., Bruns, D. R., Peelor, F. F., Biela, L. M., Miller, R. A., Hamilton, K. L., & Miller, B. F. (2014). Long-lived crowded-litter mice have an age-dependent increase in protein synthesis to DNA synthesis ratio and mTORC1 substrate phosphorylation. AJP: Endocrinology and Metabolism, 307(9), E813–E821. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00256.2014
Moore, C. D., Crocker, D. E., Fahlman, A., Moore, M. J., Willoughby, D. S., Robbins, K. A., Kanatous, S. B., & Trumble, S. J. (2014). Ontogenetic changes in skeletal muscle fiber type, fiber diameter and myoglobin concentration in the Northern elephant seal (Mirounga angustirostris). Frontiers in Physiology, 5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2014.00217
King, I. N., Yartseva, V., Salas, D., Kumar, A., Heidersbach, A., Ando, D. M., Stallings, N. R., Elliott, J. L., Srivastava, D., & Ivey, K. N. (2014). The RNA-binding Protein TDP-43 Selectively Disrupts MicroRNA-1/206 Incorporation into the RNA-induced Silencing Complex. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 289(20), 14263–14271. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.561902
van der Plas-Duivesteijn, S. J., Mohammed, Y., Dalebout, H., Meijer, A., Botermans, A., Hoogendijk, J. L., Henneman, A. A., Deelder, A. M., Spaink, H. P., & Palmblad, M. (2014). Identifying Proteins in Zebrafish Embryos Using Spectral Libraries Generated from Dissected Adult Organs and Tissues. Journal of Proteome Research, 13(3), 1537–1544. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr4010585
Verhaart, I. E. C., van Vliet-van den Dool, L., Sipkens, J. A., de Kimpe, S. J., Kolfschoten, I. G. M., van Deutekom, J. C. T., Liefaard, L., Ridings, J. E., Hood, S. R., & Aartsma-Rus, A. (2014). The Dynamics of Compound, Transcript, and Protein Effects After Treatment With 2OMePS Antisense Oligonucleotides in mdx Mice. Molecular Therapy—Nucleic Acids, 3(2), e148. https://doi.org/10.1038/mtna.2014.1
Mathewson, M. A., Chambers, H. G., Girard, P. J., Tenenhaus, M., Schwartz, A. K., & Lieber, R. L. (2014). Stiff muscle fibers in calf muscles of patients with cerebral palsy lead to high passive muscle stiffness: CP CALF MUSCLE FIBER STIFFNESS. Journal of Orthopaedic Research, 32(12), 1667–1674. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.22719
Lashgari, M., & Lee, H. K. (2014). Determination of perfluorinated carboxylic acids in fish fillet by micro-solid phase extraction, followed by liquid chromatography–triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 1369, 26–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.09.082
Mukund, K., Mathewson, M., Minamoto, V., Ward, S. R., Subramaniam, S., & Lieber, R. L. (2014). Systems analysis of transcriptional data provides insights into muscle’s biological response to botulinum toxin: Transcriptional Profiling after BoNT-A. Muscle & Nerve, 50(5), 744–758. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.24211
Menon, V., Zhi, X., Hossain, T., Bartke, A., Spong, A., Gesing, A., & Masternak, M. M. (2014). The contribution of visceral fat to improved insulin signaling in Ames dwarf mice. Aging Cell, 13(3), 497–506. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12201
Melero, M., García-Párraga, D., Corpa, J., Ortega, J., Rubio-Guerri, C., Crespo, J., Rivera-Arroyo, B., & Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J. (2014). First molecular detection and characterization of herpesvirus and poxvirus in a Pacific walrus (Odobenus rosmarus divergens). BMC Veterinary Research, 10(1), 968. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-014-0308-2
Schuh, R. A., Jackson, K. C., Schlappal, A. E., Spangenburg, E. E., Ward, C. W., Park, J. H., Dugger, N., Shi, G., & Fishman, P. S. (2014). Mitochondrial oxygen consumption deficits in skeletal muscle isolated from an Alzheimer’s disease-relevant murine model. BMC Neuroscience, 15(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2202-15-24
Drake, J. C., Peelor, F. F., Biela, L. M., Watkins, M. K., Miller, R. A., Hamilton, K. L., & Miller, B. F. (2013). Assessment of Mitochondrial Biogenesis and mTORC1 Signaling During Chronic Rapamycin Feeding in Male and Female Mice. The Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, 68(12), 1493–1501. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glt047
Erickson, A. K., & Pfeiffer, J. K. (2013). Dynamic Viral Dissemination in Mice Infected with Yellow Fever Virus Strain 17D. Journal of Virology, 87(22), 12392–12397. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.02149-13
Cheng, X., Guo, S., Liu, Y., Chu, H., Hakimi, P., Berger, N. A., Hanson, R. W., & Kao, H.-Y. (2013). Ablation of Promyelocytic Leukemia Protein (PML) Re-patterns Energy Balance and Protects Mice from Obesity Induced by a Western Diet. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 288(41), 29746–29759. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.487595
Miller, B. F., Robinson, M. M., Reuland, D. J., Drake, J. C., Peelor, F. F., Bruss, M. D., Hellerstein, M. K., & Hamilton, K. L. (2013). Calorie Restriction Does Not Increase Short-term or Long-term Protein Synthesis. The Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, 68(5), 530–538. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/gls219
Mcgowan, I., Hoesley, C., Cranston, R. D., Andrew, P., Janocko, L., Dai, J. Y., Carballo-Dieguez, A., Ayudhya, R. K. N., Piper, J., Hladik, F., & Mayer, K. (2013). A Phase 1 Randomized, Double Blind, Placebo Controlled Rectal Safety and Acceptability Study of Tenofovir 1% Gel (MTN-007). PLoS ONE, 8(4), e60147. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0060147
Moghadaszadeh, B., Rider, B. E., Lawlor, M. W., Childers, M. K., Grange, R. W., Gupta, K., Boukedes, S. S., Owen, C. A., & Beggs, A. H. (2013). Selenoprotein N deficiency in mice is associated with abnormal lung development. The FASEB Journal, 27(4), 1585–1599. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.12-212688
Gao, N., Huang, J., He, W., Zhu, M., Kamm, K. E., & Stull, J. T. (2013). Signaling through Myosin Light Chain Kinase in Smooth Muscles. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 288(11), 7596–7605. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.427112
Hanke, M. L., Heim, C. E., Angle, A., Sanderson, S. D., & Kielian, T. (2013). Targeting Macrophage Activation for the Prevention and Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Infections. The Journal of Immunology, 190(5), 2159–2168. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1202348
Frank, P., Katz, A., Andersson, E., & Sahlin, K. (2013). Acute exercise reverses starvation-mediated insulin resistance in humans. AJP: Endocrinology and Metabolism, 304(4), E436–E443. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00416.2012
Percival, J. M., Siegel, M. P., Knowels, G., & Marcinek, D. J. (2013). Defects in mitochondrial localization and ATP synthesis in the mdx mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy are not alleviated by PDE5 inhibition. Human Molecular Genetics, 22(1), 153–167. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/dds415
Riisager, M., Duno, M., Hansen, F. J., Krag, T. O., Vissing, C. R., & Vissing, J. (2013). A new mutation of the fukutin gene causing late-onset limb girdle muscular dystrophy. Neuromuscular Disorders, 23(7), 562–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nmd.2013.04.006
Brault, J. J., Pizzimenti, N. M., Dentel, J. N., & Wiseman, R. W. (2013). Selective inhibition of ATPase activity during contraction alters the activation of p38 MAP kinase isoforms in skeletal muscle. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 114(6), 1445–1455. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.24486
Veltrop, M., van der Kaa, J., Claassens, J., van Vliet, L., Verbeek, S., & Aartsma-Rus, A. (2013). Generation of Embryonic Stem Cells and Mice for Duchenne Research. PLoS Currents. https://doi.org/10.1371/currents.md.cbf1d33001de80923ce674302cad7925
Liu, B.-H., Lin, Y.-Y., Wang, Y.-C., Huang, C.-W., Chen, C.-C., Wu, S.-C., Mersmann, H. J., Cheng, W. T. K., & Ding, S.-T. (2013). Porcine Adiponectin Receptor 1 Transgene Resists High-fat/Sucrose Diet-Induced Weight Gain, Hepatosteatosis and Insulin Resistance in Mice. Experimental Animals, 62(4), 347–360. https://doi.org/10.1538/expanim.62.347
Chaker, B., Samra, T. A., Datta, N. S., & Abou-Samra, A. B. (2013). Altered Responses to Cold Environment in Urocortin 1 and Corticotropin-Releasing Factor Deficient Mice. Physiology Journal, 2013, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/185767
Battaglia, G. M., Zheng, D., Hickner, R. C., & Houmard, J. A. (2012). Effect of exercise training on metabolic flexibility in response to a high-fat diet in obese individuals. AJP: Endocrinology and Metabolism, 303(12), E1440–E1445. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00355.2012






